Page 57 - Read Online
P. 57
Boyd et al. Art Int Surg 2024;4:316-23 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ais.2024.53 Page 320
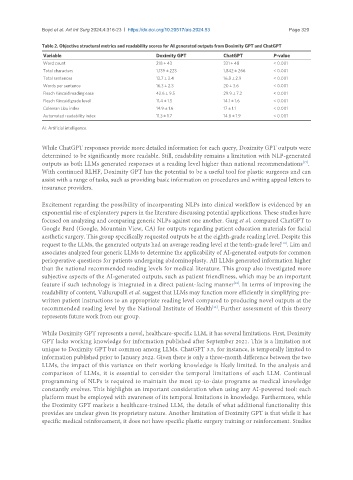
Table 2. Objective structural metrics and readability scores for AI generated outputs from Doximity GPT and ChatGPT
Variable Doximity GPT ChatGPT P-value
Word count 218 ± 43 331 ± 48 < 0.001
Total characters 1,139 ± 223 1,842 ± 266 < 0.001
Total sentences 13.7 ± 3.4 16.8 ± 2.9 < 0.001
Words per sentence 16.3 ± 2.3 20 ± 3.6 < 0.001
Flesch Kincaid reading ease 42.6 ± 9.5 29.9 ± 7.2 < 0.001
Flesch Kincaid grade level 11.4 ± 1.5 14.1 ± 1.6 < 0.001
Coleman Liau index 14.9 ± 1.6 17 ± 1.1 < 0.001
Automated readability index 11.3 ± 1.7 14.8 ± 1.9 < 0.001
AI: Artificial intelligence.
While ChatGPT responses provide more detailed information for each query, Doximity GPT outputs were
determined to be significantly more readable. Still, readability remains a limitation with NLP-generated
outputs as both LLMs generated responses at a reading level higher than national recommendations .
[17]
With continued RLHF, Doximity GPT has the potential to be a useful tool for plastic surgeons and can
assist with a range of tasks, such as providing basic information on procedures and writing appeal letters to
insurance providers.
Excitement regarding the possibility of incorporating NLPs into clinical workflow is evidenced by an
exponential rise of exploratory papers in the literature discussing potential applications. These studies have
focused on analyzing and comparing generic NLPs against one another. Garg et al. compared ChatGPT to
Google Bard (Google, Mountain View, CA) for outputs regarding patient education materials for facial
aesthetic surgery. This group specifically requested outputs be at the eighth-grade reading level. Despite this
[18]
request to the LLMs, the generated outputs had an average reading level at the tenth-grade level . Lim and
associates analyzed four generic LLMs to determine the applicability of AI-generated outputs for common
perioperative questions for patients undergoing abdominoplasty. All LLMs generated information higher
than the national recommended reading levels for medical literature. This group also investigated more
subjective aspects of the AI-generated outputs, such as patient friendliness, which may be an important
feature if such technology is integrated in a direct patient-facing manner . In terms of improving the
[12]
readability of content, Vallurupalli et al. suggest that LLMs may function more efficiently in simplifying pre-
written patient instructions to an appropriate reading level compared to producing novel outputs at the
[11]
recommended reading level by the National Institute of Health . Further assessment of this theory
represents future work from our group.
While Doximity GPT represents a novel, healthcare-specific LLM, it has several limitations. First, Doximity
GPT lacks working knowledge for information published after September 2021. This is a limitation not
unique to Doximity GPT but common among LLMs. ChatGPT 3.5, for instance, is temporally limited to
information published prior to January 2022. Given there is only a three-month difference between the two
LLMs, the impact of this variance on their working knowledge is likely limited. In the analysis and
comparison of LLMs, it is essential to consider the temporal limitations of each LLM. Continual
programming of NLPs is required to maintain the most up-to-date programs as medical knowledge
constantly evolves. This highlights an important consideration when using any AI-powered tool: each
platform must be employed with awareness of its temporal limitations in knowledge. Furthermore, while
the Doximity GPT markets a healthcare-trained LLM, the details of what additional functionality this
provides are unclear given its proprietary nature. Another limitation of Doximity GPT is that while it has
specific medical reinforcement, it does not have specific plastic surgery training or reinforcement. Studies