Page 32 - Read Online
P. 32
Page 116 Ding et al. Art Int Surg 2024;4:109-38 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ais.2024.16
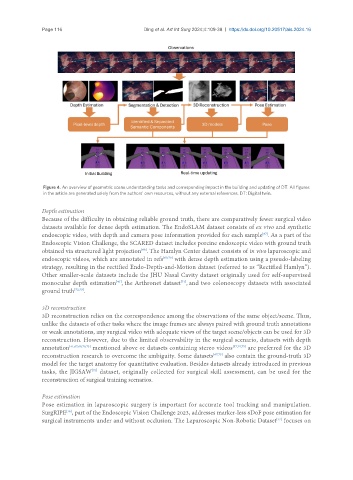
Figure 4. An overview of geometric scene understanding tasks and corresponding impact in the building and updating of DT. All figures
in the article are generated solely from the authors’ own resources, without any external references. DT: Digital twin.
Depth estimation
Because of the difficulty in obtaining reliable ground truth, there are comparatively fewer surgical video
datasets available for dense depth estimation. The EndoSLAM dataset consists of ex vivo and synthetic
endoscopic video, with depth and camera pose information provided for each sample . As a part of the
[67]
Endoscopic Vision Challenge, the SCARED dataset includes porcine endoscopic video with ground truth
obtained via structured light projection . The Hamlyn Center dataset consists of in vivo laparoscopic and
[68]
endoscopic videos, which are annotated in refs [69,70] with dense depth estimation using a pseudo-labeling
strategy, resulting in the rectified Endo-Depth-and-Motion dataset (referred to as “Rectified Hamlyn”).
Other smaller-scale datasets include the JHU Nasal Cavity dataset originally used for self-supervised
monocular depth estimation , the Arthronet dataset , and two colonoscopy datasets with associated
[71]
[41]
ground truth [72,73] .
3D reconstruction
3D reconstruction relies on the correspondence among the observations of the same object/scene. Thus,
unlike the datasets of other tasks where the image frames are always paired with ground truth annotations
or weak annotations, any surgical video with adequate views of the target scene/objects can be used for 3D
reconstruction. However, due to the limited observability in the surgical scenario, datasets with depth
annotation [41,67,69,70,73] mentioned above or datasets containing stereo videos [57,74,75] are preferred for the 3D
reconstruction research to overcome the ambiguity. Some datasets [67,73] also contain the ground-truth 3D
model for the target anatomy for quantitative evaluation. Besides datasets already introduced in previous
tasks, the JIGSAW dataset, originally collected for surgical skill assessment, can be used for the
[75]
reconstruction of surgical training scenarios.
Pose estimation
Pose estimation in laparoscopic surgery is important for accurate tool tracking and manipulation.
SurgRIPE , part of the Endoscopic Vision Challenge 2023, addresses marker-less 6DoF pose estimation for
[76]
surgical instruments under and without occlusion. The Laparoscopic Non-Robotic Dataset focuses on
[77]