Page 58 - Read Online
P. 58
Zanello et al. Rare Dis Orphan Drugs J 2023;2:9 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/rdodj.2023.04 Page 5 of 15
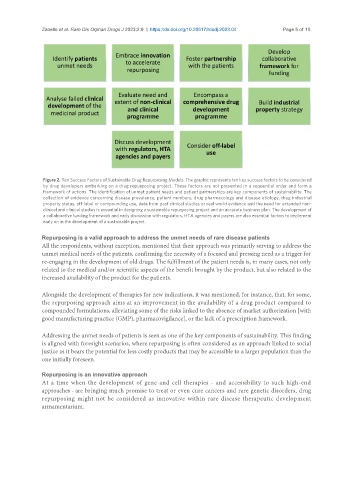
Figure 2. Ten Success Factors of Sustainable Drug Repurposing Models. The graphic represents ten key success factors to be considered
by drug developers embarking on a drug repurposing project. These factors are not presented in a sequential order and form a
framework of actions. The identification of unmet patient needs and patient partnerships are key components of sustainability. The
collection of evidence concerning disease prevalence, patient numbers, drug pharmacology and disease etiology, drug industrial
property status, off-label or compounding use, data from past clinical studies or real world evidence and the need for extended non-
clinical and clinical studies is essential in designing a sustainable repurposing project and an accurate business plan. The development of
a collaborative funding framework and early discussion with regulators, HTA agencies and payers are also essential factors to implement
early on in the development of a sustainable project.
Repurposing is a valid approach to address the unmet needs of rare disease patients
All the respondents, without exception, mentioned that their approach was primarily serving to address the
unmet medical needs of the patients, confirming the necessity of a focused and pressing need as a trigger for
re-engaging in the development of old drugs. The fulfillment of the patient needs is, in many cases, not only
related to the medical and/or scientific aspects of the benefit brought by the product, but also related to the
increased availability of the product for the patients.
Alongside the development of therapies for new indications, it was mentioned, for instance, that, for some,
the repurposing approach aims at an improvement in the availability of a drug product compared to
compounded formulations, alleviating some of the risks linked to the absence of market authorization [with
good manufacturing practice (GMP), pharmacovigilance], or the lack of a prescription framework.
Addressing the unmet needs of patients is seen as one of the key components of sustainability. This finding
is aligned with foresight scenarios, where repurposing is often considered as an approach linked to social
justice as it bears the potential for less costly products that may be accessible to a larger population than the
one initially foreseen.
Repurposing is an innovative approach
At a time when the development of gene and cell therapies - and accessibility to such high-end
approaches - are bringing much promise to treat or even cure cancers and rare genetic disorders, drug
repurposing might not be considered as innovative within rare disease therapeutic development
armamentarium.