Page 124 - Read Online
P. 124
Page 6 of 19 Lee et al. Microstructures 2023;3:2023021 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/microstructures.2023.08
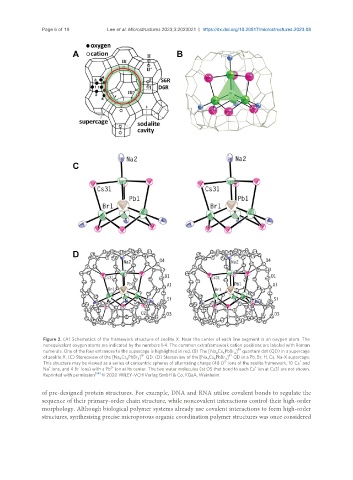
Figure 2. (A) Schematics of the framework structure of zeolite X. Near the center of each line segment is an oxygen atom. The
nonequivalent oxygen atoms are indicated by the numbers 1-4. The common extraframework cation positions are labeled with Roman
8+
numerals. One of the four entrances to the supercage is highlighted in red. (B) The [Na Cs PbBr ] quantum dot (QD) in a supercage
4 6 4
8+
8+
of zeolite X. (C) Stereoview of the [Na Cs PbBr ] QD. (D) Stereoview of the [Na Cs PbBr ] QD in a Pb, Br, H, Cs, Na-X supercage.
4
6
4
4
4
6
2-
+
This structure may be viewed as a series of concentric spheres of alternating charge (48 O ions of the zeolite framework, 10 Cs and
+
+
-
2+
Na ions, and 4 Br ions) with a Pb ion at its center. The two water molecules (at O5 that bond to each Cs ion at Cs31 are not shown.
Reprinted with permission [54] © 2020 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
of pre-designed protein structures. For example, DNA and RNA utilise covalent bonds to regulate the
sequence of their primary-order chain structure, while noncovalent interactions control their high-order
morphology. Although biological polymer systems already use covalent interactions to form high-order
structures, synthesising precise microporous organic coordination polymer structures was once considered