Page 379 - Read Online
P. 379
Page 4 of 7 Di Marco et al. Vessel Plus 2020;4:32 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2020.23
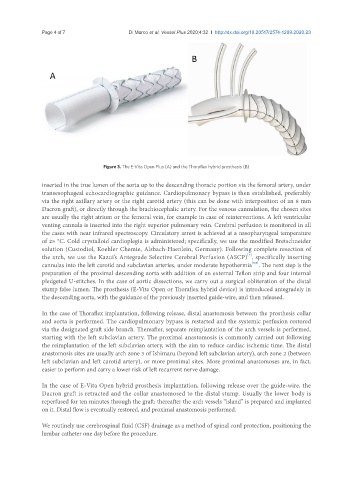
Figure 3. The E-Vita Open Plus (A) and the Thoraflex hybrid prosthesis (B)
inserted in the true lumen of the aorta up to the descending thoracic portion via the femoral artery, under
transesophageal echocardiographic guidance. Cardiopulmonary bypass is then established, preferably
via the right axillary artery or the right carotid artery (this can be done with interposition of an 8 mm
Dacron graft), or directly through the brachiocephalic artery. For the venous cannulation, the chosen sites
are usually the right atrium or the femoral vein, for example in case of reinterventions. A left ventricular
venting cannula is inserted into the right superior pulmonary vein. Cerebral perfusion is monitored in all
the cases with near infrared spectroscopy. Circulatory arrest is achieved at a nasopharyngeal temperature
of 25 °C. Cold crystalloid cardioplegia is administered; specifically, we use the modified Bretschneider
solution (Custodiol, Koehler Chemie, Alsbach-Haenlein, Germany). Following complete resection of
[7]
the arch, we use the Kazui’s Antegrade Selective Cerebral Perfusion (ASCP) , specifically inserting
[8,9]
cannulas into the left carotid and subclavian arteries, under moderate hypothermia . The next step is the
preparation of the proximal descending aorta with addition of an external Teflon strip and four internal
pledgeted U-stitches. In the case of aortic dissections, we carry out a surgical obliteration of the distal
stump false lumen. The prosthesis (E-Vita Open or Thoraflex hybrid device) is introduced antegradely in
the descending aorta, with the guidance of the previously inserted guide-wire, and then released.
In the case of Thoraflex implantation, following release, distal anastomosis between the prosthesis collar
and aorta is performed. The cardiopulmonary bypass is restarted and the systemic perfusion restored
via the designated graft side branch. Thereafter, separate reimplantation of the arch vessels is performed,
starting with the left subclavian artery. The proximal anastomosis is commonly carried out following
the reimplantation of the left subclavian artery, with the aim to reduce cardiac ischemic time. The distal
anastomosis sites are usually arch zone 3 of Ishimaru (beyond left subclavian artery), arch zone 2 (between
left subclavian and left carotid artery), or more proximal sites. More proximal anastomoses are, in fact,
easier to perform and carry a lower risk of left recurrent nerve damage.
In the case of E-Vita Open hybrid prosthesis implantation, following release over the guide-wire, the
Dacron graft is retracted and the collar anastomosed to the distal stump. Usually the lower body is
reperfused for ten minutes through the graft; thereafter the arch vessels “island” is prepared and implanted
on it. Distal flow is eventually restored, and proximal anastomosis performed.
We routinely use cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) drainage as a method of spinal cord protection, positioning the
lumbar catheter one day before the procedure.