Page 47 - Read Online
P. 47
Chávez-Castillo et al. Vessel Plus 2018;2:6 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2018.02 Page 5 of 11
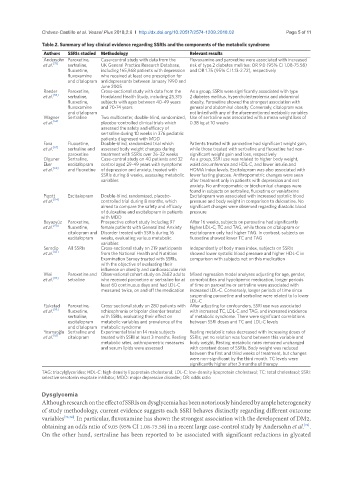
Table 2. Summary of key clinical evidence regarding SSRIs and the components of the metabolic syndrome
Authors SSRIs studied Methodology Relevant results
Andersohn Paroxetine, Case-control study with data from the Fluvoxamine and paroxetine were associated with increased
et al. [75] sertraline, UK General Practice Research Database, risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: OR 9.0 (95% CI 1.08-75.58)
fluoxetine, including 165,968 patients with depression and OR 1.75 (95% CI 1.13-2.72), respectively
fluvoxamine who received at least one prescription for
and citalopram antidepressants between January 1990 and
June 2005
Raeder Paroxetine, Cross-sectional study with data from the As a group, SSRIs were significantly associated with type
et al. [58] sertraline, Hordaland Health Study, including 25,315 2 diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia and abdominal
fluoxetine, subjects with ages between 40-49 years obesity. Paroxetine showed the strongest association with
fluvoxamine and 70-74 years general and abdominal obesity. Conversely, citalopram was
and citalopram not linked with any of the aforementioned metabolic variables
Wagner Sertraline Two multicenter, double-blind, randomized, Use of sertraline was associated with a mean weight loss of
et al. [62] placebo-controlled clinical trials which 0.38 kg at 10 weeks
assessed the safety and efficacy of
sertraline during 10 weeks in 376 pediatric
patients diagnosed with MDD
Fava Fluoxetine, Double-blind, randomized trial which Patients treated with paroxetine had significant weight gain,
et al. [67] sertraline and assessed body weight changes during while those treated with sertraline and fluoxetine had non-
paroxetine treatment with SSRIs over 26-32 weeks significant weight gain and loss, respectively
Olguner Sertraline, Case-control study on 40 patients and 32 As a group, SSRI use was related to higher body weight,
Eker escitalopram control aged 29-49 years with symptoms waist circumference and HDL-C, and lower insulin and
et al. [66] and fluoxetine of depression and anxiety, treated with HOMA index levels. Escitalopram was also associated with
SSRIs during 8 weeks, assessing metabolic lower fasting glucose. Anthropometric changes were seen
variables after treatment only in patients with depression and not
anxiety. No anthropometric or biochemical changes were
found in subjects on sertraline, fluoxetine or venlafaxine
Pigott Escitalopram Double-blind, randomized, placebo- Escitalopram was associated with increased systolic blood
et al. [114] controlled trial during 8 months, which pressure and body weight in comparison to duloxetine. No
aimed to compare the safety and efficacy significant changes were observed regarding diastolic blood
of duloxetine and escitalopram in patients pressure
with MDD
Beyazyüz Paroxetine, Prospective cohort study including 97 After 16 weeks, subjects on paroxetine had significantly
et al. [90] fluoxetine, female patients with Generalized Anxiety higher LDL-C, TC and TAG, while those on citalopram or
citalopram and Disorder treated with SSRIs during 16 escitalopram only had higher TAG. In contrast, subjects on
escitalopram weeks, evaluating various metabolic fluoxetine showed lower TC and TAG
variables
Serodio All SSRIs Cross-sectional study on 219 participants Independently of body mass index, subjects on SSRIs
et al. [85] from the National Health and Nutrition showed lower systolic blood pressure and higher HDL-C in
Examination Survey treated with SSRIs, comparison with subjects not on this medication
with the objective of evaluating their
influence on obesity and cardiovascular risk
Wei Paroxetine and Observational cohort study on 2682 adults Mixed regression model analyses adjusting for age, gender,
et al. [89] setraline who received paroxetine or sertraline for at comorbidities and hypolipemic medication, longer periods
least 60 continuous days and had LDL-C of time on paroxetine or sertraline were associated with
measured twice, on and off the medication increased LDL-C. Conversely, longer periods of time since
suspending paroxetine and sertraline were related to lo lower
LDL-C
Fjukstad Paroxetine, Cross-sectional study on 280 patients with After adjusting for confounders, SSRI use was associated
et al. [99] fluoxetine, schizophrenia or bipolar disorder treated with increased TC, LDL-C and TAG, and increased incidence
sertraline, with SSRIs, evaluating their effect on of metabolic syndrome. There were significant correlations
escitalopram metabolic variables and prevalence of the between SSRI doses and TC and LDL-C levels
and citalopram metabolic syndrome
Yosmaoğlu Sertraline and Experimental trial on 14 male subjects Resting metabolic rates decreased with increasing doses of
et al. [83] citalopram treated with SSRI at least 3 months. Resting SSRIs, yet no relation was found between this variable and
metabolic rates, anthropometric measures body weight. Resting metabolic rates remained unchanged
and serum lipids were assessed with constant doses of SSRIs. Body weight was reduced
between the first and third weeks of treatment, but changes
were non-significant by the third month. TC levels were
significantly higher after 3 months of therapy
TAG: triacylglycerides; HDL-C: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TC: total cholesterol; SSRI:
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; MDD: major depressive disorder; OR: odds ratio
Dysglycemia
Although research on the effect of SSRIs on dysglycemia has been notoriously hindered by ample heterogeneity
of study methodology, current evidence suggests each SSRI behaves distinctly regarding different outcome
variables [73,74] . In particular, fluvoxamine has shown the strongest association with the development of DM2,
obtaining an odds ratio of 9.05 (95% CI 1.08-75.58) in a recent large case-control study by Andersohn et al. .
[75]
On the other hand, sertraline has been reported to be associated with significant reductions in glycated