Page 11 - Read Online
P. 11
Page 4 of 13 Carciotto et al. Vessel Plus 2024;8:33 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2024.01
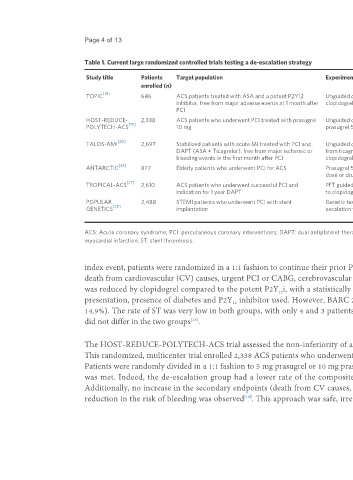
Table 1. Current large randomized controlled trials testing a de-escalation strategy
Study title Patients Target population Experimental treatment Control treatment Primary endpoint (experimental group vs. control group, P-
enrolled (n) value)
[18]
TOPIC 646 ACS patients treated with ASA and a potent P2Y12 Unguided de-escalation to Continuation of Composite of CV death, urgent coronary revascularization,
inhibitor, free from major adverse events at 1 month after clopidogrel ticagrelor or prasugrel stroke, BARC ≥ 2 bleedings at 12 months (13.4% vs. 26.3%, P <
PCI 0.01)
HOST-REDUCE- 2,338 ACS patients who underwent PCI treated with prasugrel Unguided de-escalation to Continuation of Net adverse clinical events: all-cause death, nonfatal MI, ST,
[19]
POLYTECH-ACS 10 mg prasugrel 5 mg prasugrel 10 mg revascularization, stroke, BARC ≥ 2 bleedings at 12 months (7.2%
vs. 10.1%, P < 0.0001)
non-inferiority
[20]
TALOS-AMI 2,697 Stabilized patients with acute MI treated with PCI and Unguided de-escalation Continuation of Composite of CV death, MI, stroke or BARC ≥ 2 type bleeding at
DAPT (ASA + Ticagrelor), free from major ischemic or from ticagrelor to ticagrelor 12 months (4.6% vs. 8.4%, P < 0.001)
bleeding events in the first month after PCI clopidogrel
[26]
ANTARCTIC 877 Elderly patients who underwent PCI for ACS Prasugrel 5 mg with PFT Prasugrel 5 mg with Composite of CV death, MI, stroke, ST, urgent revascularization,
dose or drug adjustment no PFT BARC 2, 3 or 5 bleeding complications (28% vs. 28%, P = 0.98)
[27]
TROPICAL-ACS 2,610 ACS patients who underwent successful PCI and PFT guided de-escalation Standard DAPT (ASA Net clinical benefit: CV death, MI, stroke or BARC 2 or higher
indication for 1 year DAPT to clopidogrel + Prasugrel 10 mg) bleeding events (7% vs. 9%, P = 0.0004)
non-inferiority
POPULAR 2,488 STEMI patients who underwent PCI with stent Genetic test guided de- Continuation of Net adverse clinical events: death from any cause, MI, definite ST,
[28]
GENETICS implantation escalation to clopidogrel ticagrelor or prasugrel cerebrovascular events or PLATO major bleeding at 12 months
(5.1% vs. 5.9%, P non-inferiority < 0.001)
ACS: Acute coronary syndrome; PCI: percutaneous coronary interventions; DAPT: dual antiplatelet therapy; PFT: platelet function tests; CV: cardiovascular; BARC: bleeding academic research consortium; MI:
myocardial infarction; ST: stent thrombosis.
index event, patients were randomized in a 1:1 fashion to continue their prior P2Y i or to switch to clopidogrel. The rate of the primary composite endpoint of
12
death from cardiovascular (CV) causes, urgent PCI or CABG, cerebrovascular events, and BARC type 2 or more serious bleeding at 12 months after the ACS
was reduced by clopidogrel compared to the potent P2Y i, with a statistically significant difference (13.4% vs. 26.3%). This result was consistent across ACS
12
presentation, presence of diabetes and P2Y inhibitor used. However, BARC 2 or higher bleeding events were less frequent in the clopidogrel group (4% vs.
12
14.9%). The rate of ST was very low in both groups, with only 4 and 3 patients experiencing it, respectively. Additionally, the rate of ischemic complications
did not differ in the two groups .
[18]
[19]
The HOST-REDUCE-POLYTECH-ACS trial assessed the non-inferiority of a DAPT de-escalation strategy based on the reduction of the prasugrel dose .
This randomized, multicenter trial enrolled 2,338 ACS patients who underwent PCI and met the core indication for treatment with prasugrel-based DAPT .
[19]
Patients were randomly divided in a 1:1 fashion to 5 mg prasugrel or 10 mg prasugrel after the initial 30 days of 10 mg prasugrel treatment. The non-inferiority
was met. Indeed, the de-escalation group had a lower rate of the composite primary endpoint of net adverse clinical events at 1 year (7.2% vs. 10.1%).
Additionally, no increase in the secondary endpoints (death from CV causes, MI, ST, and ischemic cerebrovascular events) was registered and a significant
reduction in the risk of bleeding was observed . This approach was safe, irrespective of PCI complexity. Indeed, 705 patients received complex PCI, and a
[19]