Page 30 - Read Online
P. 30
Jubouri et al. Vessel Plus 2023;7:5 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2022.49 Page 9 of 13
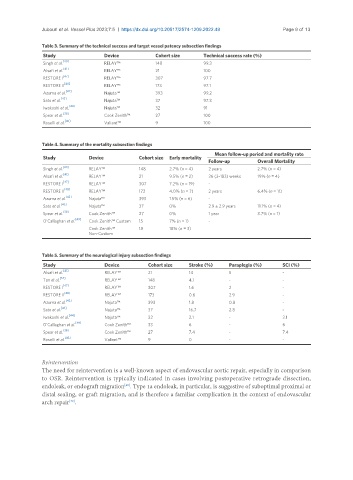
Table 3. Summary of the technical success and target vessel patency subsection findings
Study Device Cohort size Technical success rate (%)
Singh et al. [40] RELAY™ 148 99.3
[41]
Alsafi et al. RELAY™ 21 100
[47]
RESTORE I RELAY™ 307 97.7
[48]
RESTORE II RELAY™ 173 97.1
[42]
Azuma et al. Najuta™ 393 99.2
Sato et al. [43] Najuta™ 37 97.3
[44]
Iwakoshi et al. Najuta™ 32 91
Spear et al. [38] Cook Zenith™ 27 100
[45]
Roselli et al. Valiant™ 9 100
Table 4. Summary of the mortality subsection findings
Mean follow-up period and mortality rate
Study Device Cohort size Early mortality
Follow-up Overall Mortality
Singh et al. [40] RELAY™ 148 2.7% (n = 4) 2 years 2.7% (n = 4)
[41]
Alsafi et al. RELAY™ 21 9.5% (n = 2) 36 (3-183) weeks 19% (n = 4)
RESTORE I [47] RELAY™ 307 7.2% (n = 19) -
[48]
RESTORE II RELAY™ 173 4.0% (n = 7) 2 years 6.4% (n = 11)
Azuma et al. [42] Najuta™ 393 1.5% (n = 6) -
[43]
Sato et al. Najuta™ 37 0% 2.9 ± 2.9 years 11.1% (n = 4)
[38]
Spear et al. Cook Zenith™ 27 0% 1 year 3.7% (n = 1)
O’Callaghan et al. [49] Cook Zenith™ Custom 15 7% (n = 1) -
Cook Zenith™ 18 18% (n = 3)
Non-Custom
Table 5. Summary of the neurological injury subsection findings
Study Device Cohort size Stroke (%) Paraplegia (%) SCI (%)
[41]
Alsafi et al. RELAY™ 21 14 5 -
Tan et al. [54] RELAY™ 148 4.1 - -
[47]
RESTORE I RELAY™ 307 1.6 2 -
RESTORE II [48] RELAY™ 173 0.6 2.9 -
[42]
Azuma et al. Najuta™ 393 1.8 0.8 -
Sato et al. [43] Najuta™ 37 16.7 2.8 -
[44]
Iwakoshi et al. Najuta™ 32 3.1 - 3.1
[49]
O’Callaghan et al. Cook Zenith™ 33 6 - 6
Spear et al. [38] Cook Zenith™ 27 7.4 - 7.4
[45]
Roselli et al. Valient™ 9 0 - -
Reintervention
The need for reintervention is a well-known aspect of endovascular aortic repair, especially in comparison
to OSR. Reintervention is typically indicated in cases involving postoperative retrograde dissection,
[40]
endoleak, or endograft migration . Type 1a endoleak, in particular, is suggestive of suboptimal proximal or
distal sealing, or graft migration, and is therefore a familiar complication in the context of endovascular
[40]
arch repair .