Page 192 - Read Online
P. 192
Levy et al. Vessel Plus 2024;8:4 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2023.55 Page 7 of 15
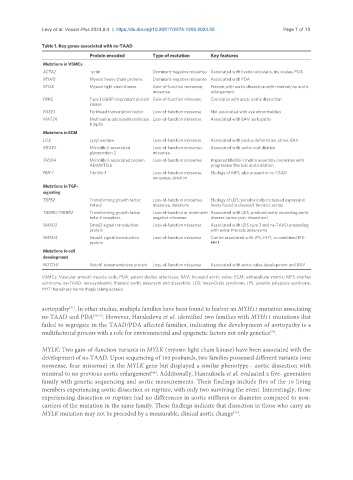
Table 1. Key genes associated with ns-TAAD
Protein encoded Type of mutation Key features
Mutations in VSMCs
ACTA2 -actin Dominant-negative missense Associated with livedo reticularis, iris oculae, PDA
MYH11 Myosin heavy chain proteins Dominant-negative missense Associated with PDA
MYLK Myosin light chain kinase Gain-of-function nonsense, Present with aortic dissection with minimal/no aortic
missense enlargement
PRKG Type I cGMP-dependent protein Gain-of-function missense Correlates with acute aortic dissection
kinase
FOXE3 Forkhead transcription factor Loss-of-function missense Not associated with eye abnormalities
MAT2A Methionine adenosyltransferase Loss-of-function missense Associated with BAV aortopathy
II alpha
Mutations in ECM
LOX Lysyl oxidase Loss-of-function missense Associated with pectus deformities, striae, BAV
MFAP5 Microfibril-associated Loss-of-function nonsense, Associated with aortic root dilation
glycoprotein 2 missense
THSD4 Microfibril-associated protein Loss-of-function nonsense Impaired fibrillin-1 matrix assembly correlates with
ADAMTSL6 progressive thoracic aorta dilation
FBN-1 Fibrillin-1 Loss-of-function missense, Etiology of MFS, also present in ns-TAAD
nonsense, deletion
Mutations in TGF-
signaling
TGFB2 Transforming growth factor Loss-of-function nonsense, Etiology of LDS; paradoxically increased expression
beta-2 missense, deletions levels found in diseased thoracic aortas
TGFBR1/TGFBR2 Transforming growth factor Loss-of-function or dominant- Associated with LDS; predominantly ascending aortic
beta-2 receptors negative missense disease (aneurysm, dissection)
SMAD3 Smad3 signal transduction Loss-of-function missense Associated with LDS type 3 and ns-TAAD presenting
protein with extra-thoracic aneurysms
SMAD4 Smad4 signal transduction Loss-of-function missense Can be associated with JPS, HHT, or combined JPS-
protein HHT
Mutations in cell
development
NOTCH1 Notch1 transmembrane protein Loss-of-function missense Associated with aortic valve development and BAV
VSMCs: Vascular smooth muscle cells; PDA: patent ductus arteriosus; BAV: bicuspid aortic valve; ECM: extracellular matrix; MFS: marfan
syndrome; ns-TAAD: non-syndromic thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection; LDS: loeys-Dietz syndrome; JPS: juvenile polyposis syndrome;
HHT: hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.
aortopathy . In other studies, multiple families have been found to harbor an MYH11 mutation associating
[41]
ns-TAAD and PDA [39,42] . However, Harakalova et al. identified two families with MYH11 mutations that
failed to segregate in the TAAD/PDA affected families, indicating the development of aortopathy is a
multifactorial process with a role for environmental and epigenetic factors not only genetics .
[43]
MYLK: Two gain-of-function variants in MYLK (myosin light chain kinase) have been associated with the
development of ns-TAAD. Upon sequencing of 193 probands, two families possessed different variants (one
nonsense, four missense) in the MYLK gene but displayed a similar phenotype - aortic dissection with
minimal to no previous aortic enlargement . Additionally, Hannuksela et al. evaluated a five- generation
[44]
family with genetic sequencing and aortic measurements. Their findings include five of the 19 living
members experiencing aortic dissection or rupture, with only two surviving the event. Interestingly, those
experiencing dissection or rupture had no differences in aortic stiffness or diameter compared to non-
carriers of the mutation in the same family. These findings indicate that dissection in those who carry an
[45]
MYLK mutation may not be preceded by a measurable, clinical aortic change .