Page 15 - Read Online
P. 15
Page 10 of 16 Katz et al. Vessel Plus 2023;7:1 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2022.52
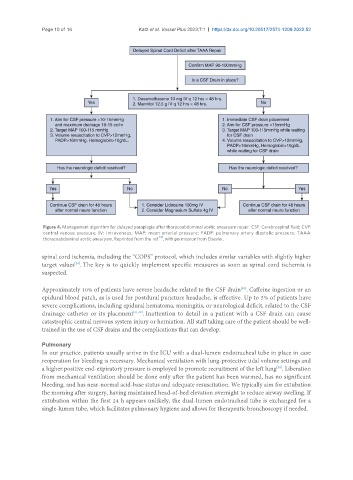
Figure 4. Management algorithm for delayed paraplegia after thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm repair. CSF: Cerebrospinal fluid; CVP:
central venous pressure; IV: intravenous; MAP: mean arterial pressure; PADP: pulmonary artery diastolic pressure; TAAA:
[2]
thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm. Reprinted from the ref. , with permission from Elsevier.
spinal cord ischemia, including the “COPS” protocol, which includes similar variables with slightly higher
target values . The key is to quickly implement specific measures as soon as spinal cord ischemia is
[39]
suspected.
[40]
Approximately 10% of patients have severe headache related to the CSF drain . Caffeine ingestion or an
epidural blood patch, as is used for postdural puncture headache, is effective. Up to 5% of patients have
severe complications, including epidural hematoma, meningitis, or neurological deficit, related to the CSF
drainage catheter or its placement [41,42] . Inattention to detail in a patient with a CSF drain can cause
catastrophic central nervous system injury or herniation. All staff taking care of the patient should be well-
trained in the use of CSF drains and the complications that can develop.
Pulmonary
In our practice, patients usually arrive in the ICU with a dual-lumen endotracheal tube in place in case
reoperation for bleeding is necessary. Mechanical ventilation with lung-protective tidal volume settings and
a higher positive end-expiratory pressure is employed to promote recruitment of the left lung . Liberation
[38]
from mechanical ventilation should be done only after the patient has been warmed, has no significant
bleeding, and has near-normal acid-base status and adequate resuscitation. We typically aim for extubation
the morning after surgery, having maintained head-of-bed elevation overnight to reduce airway swelling. If
extubation within the first 24 h appears unlikely, the dual-lumen endotracheal tube is exchanged for a
single-lumen tube, which facilitates pulmonary hygiene and allows for therapeutic bronchoscopy if needed.