Page 56 - Read Online
P. 56
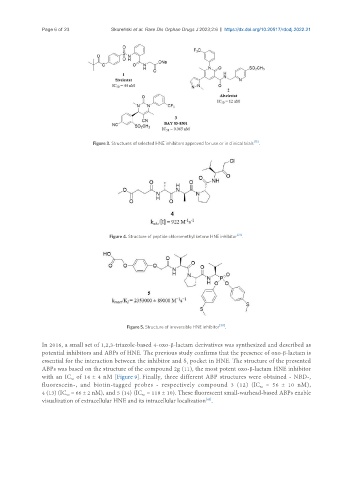
Page 6 of 23 Skoreński et al. Rare Dis Orphan Drugs J 2023;2:6 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/rdodj.2022.21
Figure 3. Structures of selected HNE inhibitors approved for use or in clinical trials [15] .
Figure 4. Structure of peptide chloromethyl ketone HNE inhibitor [37] .
Figure 5. Structure of irreversible HNE inhibitor [38] .
In 2016, a small set of 1,2,3-triazole-based 4-oxo-β-lactam derivatives was synthesized and described as
potential inhibitors and ABPs of HNE. The previous study confirms that the presence of oxo-β-lactam is
essential for the interaction between the inhibitor and S pocket in HNE. The structure of the presented
1
ABPs was based on the structure of the compound 2g (11), the most potent oxo-β-lactam HNE inhibitor
with an IC of 14 ± 4 nM [Figure 9]. Finally, three different ABP structures were obtained - NBD-,
50
fluorescein-, and biotin-tagged probes - respectively compound 3 (12) (IC = 56 ± 10 nM),
50
4 (13) (IC = 66 ± 2 nM), and 5 (14) (IC = 118 ± 10). These fluorescent small-warhead-based ABPs enable
50
50
[43]
visualization of extracellular HNE and its intracellular localization .