Page 566 - Read Online
P. 566
Page 4 of 12 Chen et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2020;7:49 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2020.28
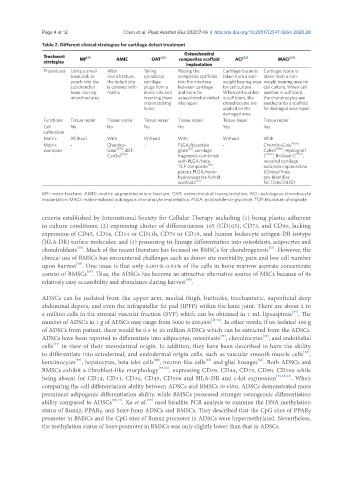
Table 2. Different clinical strategies for cartilage defect treatment
Osteochondral
Treatment [21] [22] [23] [24]
strategies MF AMIC OAT composites scaffold ACI MACI
implantation
Procedures Using a small After Taking Placing the Cartilage tissue is Cartilage tissue is
bone pick to microfracture, cylindrical composite scaffolds taken from a non- taken from a non-
punch into the the defect site cartilage into the interface weight bearing area weight bearing area for
subchondral is covered with plugs from a between cartilage for cell culture. cell culture. When cell
bone causing matrix donor site and and bone for When cell number number is sufficient,
microfractures inserting them osteochondral defect is sufficient, the the chondrocytes are
into matching site repair chondrocytes are seeded onto a scaffold
holes applied on the for damaged area repair
damaged area
Functions Tissue repair Tissue repair Tissue repair Tissue repair Tissue repair Tissue repair
Cell No No No No Yes Yes
cultivation
Matrix Without With Without With Without With
Matrix - Chondro- - PLGA/bioactive - Chondro-Gide ®[84] ,
examples Gide ®[79] , BST- glass [81] , cartilage CaReS ®[85] , Hyalograft
CarGel ®[80] fragments combined C ®[86] , BioSeed-C ®[87] ,
with PLGA/beta- recycled cartilage
TCP composite [82] , auto/allo implantation
porous PLGA/nano- (ClinicalTrials.
hydroxyapatite hybrid gov Identifier:
scaffolds [83] NCT03672825)
MF: micro-fracture; AMIC: matrix augmented micro fracture; OAT: osteochondral transplantation; ACI: autologous chondrocyte
implantation; MACI: matrix-induced autologous chondrocyte implantation; PLGA: polylactide-co-glycolide; TCP: tricalcium phosphate
criteria established by International Society for Cellular Therapy including (1) being plastic-adherent
in culture conditions; (2) expressing cluster of differentiation 105 (CD105), CD73, and CD90, lacking
expression of CD45, CD34, CD14 or CD11b, CD79 or CD19, and human leukocyte antigen-DR isotype
(HLA-DR) surface molecules; and (3) possessing tri-lineage differentiation into osteoblasts, adipocytes and
[27]
[26]
chondroblasts . Much of the recent literature has focused on BMSCs for chondrogenesis . However, the
clinical use of BMSCs has encountered challenges such as donor site morbidity, pain and low cell number
[28]
upon harvest . One issue is that only 0.001%-0.01% of the cells in bone marrow aspirate concentrate
consist of BMSCs . Thus, the ADSCs has become an attractive alternative source of MSCs because of its
[29]
[30]
relatively easy accessibility and abundance during harvest .
ADSCs can be isolated from the upper arm, medial thigh, buttocks, trochanteric, superficial deep
abdominal depots, and even the infrapatellar fat pad (IPFP) within the knee joint. There are about 2 to
[31]
6 million cells in the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) which can be obtained in 1 mL lipoaspirate . The
number of ADSCs in 1 g of ADSCs may range from 5000 to 200,000 [32-34] . In other words, if we isolated 100 g
of ADSCs from patient, there would be 0.5 to 20 million ADSCs which can be extracted from the ADSCs.
ADSCs have been reported to differentiate into adipocytes, osteoblasts , chondrocytes , and endothelial
[35]
[36]
[37]
cells in view of their mesodermal origin. In addition, they have been described to have the ability
[38]
to differentiate into ectodermal, and endodermal origin cells, such as vascular smooth muscle cells ,
[41]
[40]
[42]
[39]
keratinocytes , hepatocytes, beta islet cells , neuron-like cells and glial lineages . Both ADSCs and
BMSCs exhibit a fibroblast-like morphology [35,43] , expressing CD29, CD44, CD73, CD90, CD105 while
being absent for CD14, CD31, CD34, CD45, CD106 and HLA-DR and c-kit expression [35,36,43] . When
comparing the cell differentiation ability between ADSCs and BMSCs in vitro, ADSCs demonstrated more
prominent adipogenic differentiation ability, while BMSCs possessed stronger osteogeneic differentiation
ability compared to ADSCs [35,44] . Xu et al. used bisulfite PCR analysis to examine the DNA methylation
[35]
status of Runx2, PPARγ, and Sox9 from ADSCs and BMSCs. They described that the CpG sites of PPARγ
promoter in BMSCs and the CpG sites of Runx2 promoter in ADSCs were hypermethylated. Nevertheless,
the methylation status of Sox9 promoter in BMSCs was only slightly lower than that in ADSCs.