Page 20 - Read Online
P. 20
Page 6 of 11 Patterson et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2022;9:23 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2021.117
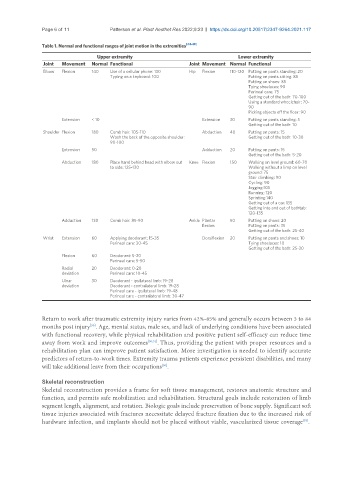
Table 1. Normal and functional ranges of joint motion in the extremities [44-49]
Upper extremity Lower extremity
Joint Movement Normal Functional Joint Movement Normal Functional
Elbow Flexion 140 Use of a cellular phone: 130 Hip Flexion 110-120 Putting on pants standing: 20
Typing on a keyboard: 100 Putting on pants sitting: 85
Putting on shoes: 85
Tying shoelaces: 90
Perineal care: 75
Getting out of the bath: 70-100
Using a standard wheelchair: 70-
90
Picking objects off the floor: 90
Extension < 10 Extension 30 Putting on pants standing: 5
Getting out of the bath: 10
Shoulder Flexion 180 Comb hair: 105-110 Abduction 40 Putting on pants: 15
Wash the back of the opposite shoulder: Getting out of the bath: 10-30
90-100
Extension 50 Adduction 20 Putting on pants: 15
Getting out of the bath: 5-20
Abduction 180 Place hand behind head with elbow out Knee Flexion 150 Walking on level ground: 60-70
to side: 125-130 Walking without a limp on level
ground: 75
Stair climbing: 90
Cycling: 90
Jogging:105
Running: 120
Sprinting:140
Getting out of a car: 135
Getting into and out of bathtub:
120-135
Adduction 130 Comb hair: 85-90 Ankle Plantar 50 Putting on shoes: 20
flexion Putting on pants: 35
Getting out of the bath: 25-40
Wrist Extension 60 Applying deodorant: 15-35 Dorsiflexion 20 Putting on pants and shoes: 10
Perineal care: 20-45 Tying shoelaces: 10
Getting out of the bath: 25-30
Flexion 60 Deodorant: 5-20
Perineal care: 5-50
Radial 20 Deodorant: 0-20
deviation Perineal care: 10-45
Ulnar 30 Deodorant - ipsilateral limb: 19-28
deviation Deodorant - contralateral limb: 19-28
Perineal care - ipsilateral limb: 19-48
Perineal care - contralateral limb: 30-47
Return to work after traumatic extremity injury varies from 42%-85% and generally occurs between 3 to 84
months post injury . Age, mental status, male sex, and lack of underlying conditions have been associated
[50]
with functional recovery, while physical rehabilitation and positive patient self-efficacy can reduce time
away from work and improve outcomes [50,51] . Thus, providing the patient with proper resources and a
rehabilitation plan can improve patient satisfaction. More investigation is needed to identify accurate
predictors of return-to-work times. Extremity trauma patients experience persistent disabilities, and many
will take additional leave from their occupations .
[50]
Skeletal reconstruction
Skeletal reconstruction provides a frame for soft tissue management, restores anatomic structure and
function, and permits safe mobilization and rehabilitation. Structural goals include restoration of limb
segment length, alignment, and rotation. Biologic goals include preservation of bone supply. Significant soft
tissue injuries associated with fractures necessitate delayed fracture fixation due to the increased risk of
hardware infection, and implants should not be placed without viable, vascularized tissue coverage .
[52]