Page 17 - Read Online
P. 17
Olcott et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2019;6:3 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2018.79 Page 5 of 7
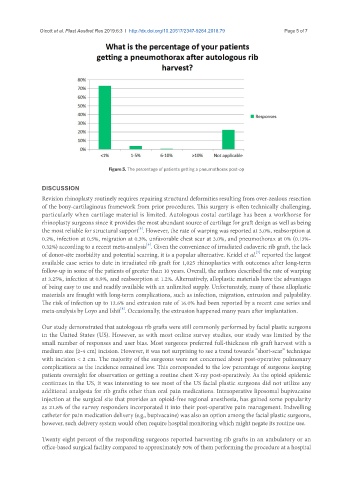
Figure 5. The percentage of patients getting a pneumothorax post-op
DISCUSSION
Revision rhinoplasty routinely requires repairing structural deformities resulting from over-zealous resection
of the bony-cartilaginous framework from prior procedures. This surgery is often technically challenging,
particularly when cartilage material is limited. Autologous costal cartilage has been a workhorse for
rhinoplasty surgeons since it provides the most abundant source of cartilage for graft design as well as being
[5]
the most reliable for structural support . However, the rate of warping was reported at 3.0%, reabsorption at
0.2%, infection at 0.5%, migration at 0.3%, unfavorable chest scar at 3.0%, and pneumothorax at 0% (0.13%-
[6]
0.32%) according to a recent meta-analysis . Given the convenience of irradiated cadaveric rib graft, the lack
[7]
of donor-site morbidity and potential scarring, it is a popular alternative. Kridel et al. reported the largest
available case series to date in irradiated rib graft for 1,025 rhinoplasties with outcomes after long-term
follow-up in some of the patients of greater than 10 years. Overall, the authors described the rate of warping
at 3.25%, infection at 0.9%, and reabsorption at 1.2%. Alternatively, alloplastic materials have the advantages
of being easy to use and readily available with an unlimited supply. Unfortunately, many of these alloplastic
materials are fraught with long-term complications, such as infection, migration, extrusion and palpability.
The risk of infection up to 12.6% and extrusion rate of 16.0% had been reported by a recent case series and
[8]
meta-analysis by Loyo and Ishii . Occasionally, the extrusion happened many years after implantation.
Our study demonstrated that autologous rib grafts were still commonly performed by facial plastic surgeons
in the United States (US). However, as with most online survey studies, our study was limited by the
small number of responses and user bias. Most surgeons preferred full-thickness rib graft harvest with a
medium size (2-4 cm) incision. However, it was not surprising to see a trend towards “short-scar” technique
with incision < 2 cm. The majority of the surgeons were not concerned about post-operative pulmonary
complications as the incidence remained low. This corresponded to the low percentage of surgeons keeping
patients overnight for observation or getting a routine chest X-ray post-operatively. As the opioid epidemic
continues in the US, it was interesting to see most of the US facial plastic surgeons did not utilize any
additional analgesia for rib grafts other than oral pain medications. Intraoperative liposomal bupivacaine
injection at the surgical site that provides an opioid-free regional anesthesia, has gained some popularity
as 21.8% of the survey responders incorporated it into their post-operative pain management. Indwelling
catheter for pain medication delivery (e.g., bupivacaine) was also an option among the facial plastic surgeons,
however, such delivery system would often require hospital monitoring which might negate its routine use.
Twenty eight percent of the responding surgeons reported harvesting rib grafts in an ambulatory or an
office-based surgical facility compared to approximately 50% of them performing the procedure at a hospital