Page 80 - Read Online
P. 80
Artiaco et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2023;10:57 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2022.145 Page 5 of 11
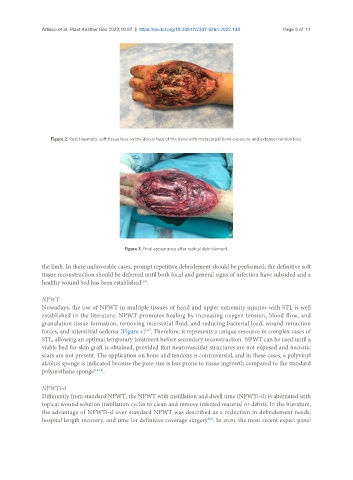
Figure 2. Post traumatic soft tissue loss on the dorsal face of the hand with metacarpal bone exposure and extensor tendon loss.
Figure 3. Final appearance after radical debridement.
the limb. In these unfavorable cases, prompt repetitive debridement should be performed; the definitive soft
tissue reconstruction should be deferred until both local and general signs of infection have subsided and a
healthy wound bed has been established .
[18]
NPWT
Nowadays, the use of NPWT in multiple tissues of hand and upper extremity injuries with STL is well
established in the literature. NPWT promotes healing by increasing oxygen tension, blood flow, and
granulation tissue formation, removing interstitial fluid, and reducing bacterial load, wound retraction
forces, and interstitial oedema [Figure 4] . Therefore, it represents a unique resource in complex cases of
[18]
STL, allowing an optimal temporary treatment before secondary reconstruction. NPWT can be used until a
viable bed for skin graft is obtained, provided that neurovascular structures are not exposed and necrotic
scars are not present. The application on bone and tendons is controversial, and in these cases, a polyvinyl
alcohol sponge is indicated because the pore size is less prone to tissue ingrowth compared to the standard
polyurethane sponge [14,19] .
NPWTi-d
Differently from standard NPWT, the NPWT with instillation and dwell time (NPWTi-d) is alternated with
topical wound solution instillation cycles to clean and remove infected material or debris. In the literature,
the advantage of NPWTi-d over standard NPWT was described as a reduction in debridement needs,
[20]
hospital length recovery, and time for definitive coverage surgery . In 2020, the most recent expert panel