Page 30 - Read Online
P. 30
Gousopoulos et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2023;10:7 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2022.101 Page 5 of 8
Table 1. Summary of clinical studies using robotic-assisted lymphatic surgery
Type Total Nr Nr of patients Time (min) for Time (min) for
Publication of Type of of with robotic Nr of robotic robotic manual Year of
publication
anastomosis
surgery
robot patients anastomosis anastomosis anastomosis
van Mulken MUSA LVAs 20 8 14 25 ± 6 min and a 9 ± 6 min and 2020
[25]
et al. range 16-33 min range 4-36 min
van Mulken MUSA LVAs 20 8 14 2021
[26]
et al.
Lindenblatt Symani LVA & 5 5 10 2022
[15]
et al. VLNT
Barbon, Symani LVA & 22 22 32 25.3 ± 12.3 min 14.1 ± 4.3 min 2022
Lindenblatt VLNT
et al. [27]
LVA: Lymphovenous anastomosis; VLNT: vascularized lymph node transfer.
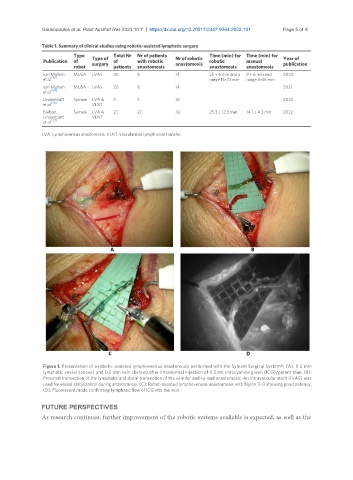
Figure 1. Presentation of a robotic-assisted lymphovenous anastomosis performed with the Symani Surgical System®. (A): 0.5 mm
lymphatic vessel (above) and 0.5 mm vein (below) after intradermal injection of 0.2 mL Indocyanine green (ICG)/patent blue. (B):
Proximal transection of the lymphatic and distal transection of the vein for end-to-end anastomosis. An intravascular stent (IVAS) was
used for vessel stabilization during anastomosis. (C): Robot-assisted lymphovenous anastomosis with Nylon 11-0 showing good patency.
(D): Fluorescent mode confirming lymphatic flow of ICG into the vein.
FUTURE PERSPECTIVES
As research continues, further improvement of the robotic systems available is expected, as well as the