Page 41 - Read Online
P. 41
Page 80 Swedberg et al. One Health Implement Res 2023;3:77-96 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ohir.2023.02
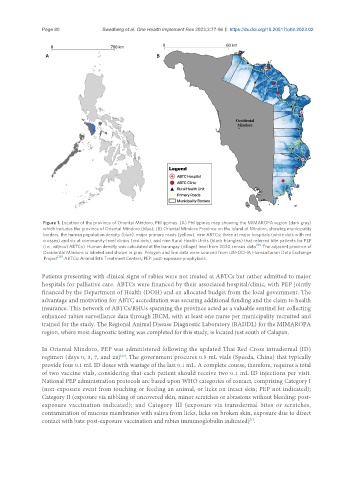
Figure 1. Location of the province of Oriental Mindoro, Philippines. (A) Philippines map showing the MIMAROPA region (dark gray)
which includes the province of Oriental Mindoro (blue); (B) Oriental Mindoro Province on the island of Mindoro, showing municipality
borders, the human population density (blue), major primary roads (yellow), nine ABTCs: three at major hospitals (white dots with red
crosses) and six at community-level clinics (red dots), and nine Rural Health Units (black triangles) that referred bite patients for PEP
(i.e., without ABTCs). Human density was calculated at the barangay (village) level from 2020 census data [18] . The adjacent province of
Occidental Mindoro is labeled and shown in gray. Polygon and line data were sourced from UN-OCHA Humanitarian Data Exchange
Project [19] . ABTCs: Animal Bite Treatment Centers; PEP: post-exposure prophylaxis.
Patients presenting with clinical signs of rabies were not treated at ABTCs but rather admitted to major
hospitals for palliative care. ABTCs were financed by their associated hospital/clinic, with PEP jointly
financed by the Department of Health (DOH) and an allocated budget from the local government. The
advantage and motivation for ABTC accreditation was securing additional funding and the claim to health
insurance. This network of ABTCs/RHUs spanning the province acted as a valuable sentinel for collecting
enhanced rabies surveillance data through IBCM, with at least one nurse per municipality recruited and
trained for the study. The Regional Animal Disease Diagnostic Laboratory (RADDL) for the MIMAROPA
region, where most diagnostic testing was completed for this study, is located just south of Calapan.
In Oriental Mindoro, PEP was administered following the updated Thai Red Cross intradermal (ID)
regimen (days 0, 3, 7, and 28) . The government procures 0.5 mL vials (Speeda, China) that typically
[20]
provide four 0.1 mL ID doses with wastage of the last 0.1 mL. A complete course, therefore, requires a total
of two vaccine vials, considering that each patient should receive two 0.1 mL ID injections per visit.
National PEP administration protocols are based upon WHO categories of contact, comprising Category I
(non-exposure event from touching or feeding an animal, or licks on intact skin; PEP not indicated);
Category II (exposure via nibbling of uncovered skin, minor scratches or abrasions without bleeding: post-
exposure vaccination indicated); and Category III (exposure via transdermal bites or scratches,
contamination of mucous membranes with saliva from licks, licks on broken skin, exposure due to direct
[1]
contact with bats: post-exposure vaccination and rabies immunoglobulin indicated) .