Page 110 - Read Online
P. 110
Rahman et al. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2018;5:14 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2017.57 Page 3 of 5
A
B C
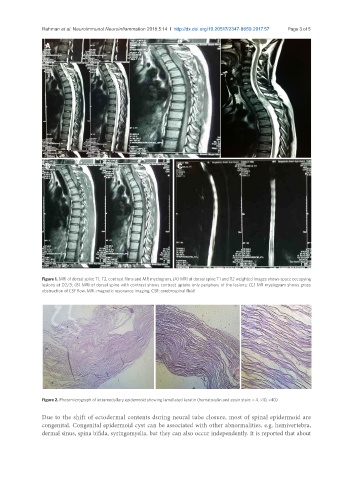
Figure 1. MRI of dorsal spine T1, T2, contrast films and MR myelogram. (A) MRI of dorsal spine T1 and T2 weighted images shows space occupying
lesions at D2/3; (B) MRI of dorsal spine with contrast shows contrast uptake only periphery of the lesions; (C) MR myelogram shows gross
obstruction of CSF flow. MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid
Figure 2. Photomicrograph of intramedullary epidermoid showing lamellated keratin (hematoxylin and eosin stain: × 4, ×10, ×40)
Due to the shift of ectodermal contents during neural tube closure, most of spinal epidermoid are
congenital. Congenital epidermoid cyst can be associated with other abnormalities, e.g. hemivertebra,
dermal sinus, spina bifida, syringomyelia, but they can also occur independently. It is reported that about