Page 44 - Read Online
P. 44
Page 6 of 8 Kuwai et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2022;6:16 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2021.122
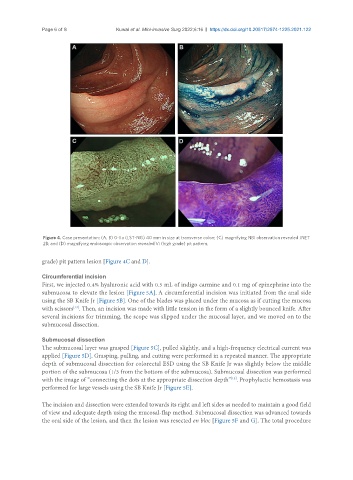
Figure 4. Case presentation: (A, B) 0-IIa (LST-NG) 40 mm in size at transverse colon; (C) magnifying NBI observation revealed JNET
2B; and (D) magnifying endoscopic observation revealed Vi (high grade) pit pattern.
grade) pit pattern lesion [Figure 4C and D].
Circumferential incision
First, we injected 0.4% hyaluronic acid with 0.5 mL of indigo carmine and 0.1 mg of epinephrine into the
submucosa to elevate the lesion [Figure 5A]. A circumferential incision was initiated from the anal side
using the SB Knife Jr [Figure 5B]. One of the blades was placed under the mucosa as if cutting the mucosa
[13]
with scissors . Then, an incision was made with little tension in the form of a slightly bounced knife. After
several incisions for trimming, the scope was slipped under the mucosal layer, and we moved on to the
submucosal dissection.
Submucosal dissection
The submucosal layer was grasped [Figure 5C], pulled slightly, and a high-frequency electrical current was
applied [Figure 5D]. Grasping, pulling, and cutting were performed in a repeated manner. The appropriate
depth of submucosal dissection for colorectal ESD using the SB Knife Jr was slightly below the middle
portion of the submucosa (1/3 from the bottom of the submucosa). Submucosal dissection was performed
with the image of “connecting the dots at the appropriate dissection depth” . Prophylactic hemostasis was
[13]
performed for large vessels using the SB Knife Jr [Figure 5E].
The incision and dissection were extended towards its right and left sides as needed to maintain a good field
of view and adequate depth using the mucosal-flap method. Submucosal dissection was advanced towards
the oral side of the lesion, and then the lesion was resected en bloc [Figure 5F and G]. The total procedure