Page 121 - Read Online
P. 121
Chen et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2021;5:54 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2021.69 Page 5 of 6
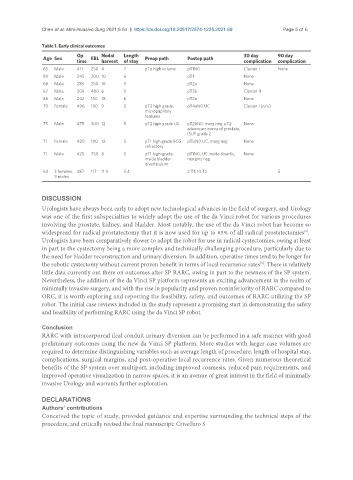
Table 1. Early clinical outcomes
Op Nodal Length 30 day 90 day
Age Sex EBL Preop path Postop path
time harvest of stay complication complication
65 Male 411 250 4 7 pTa high volume pT1N0 Clavian I None
89 Male 245 200 10 6 pT1 None
68 Male 285 250 16 5 pT2a None
67 Male 309 400 6 5 pT3b Clavian II
86 Male 242 150 18 6 pT2a None
70 Female 496 100 9 5 pT2 high grade, pT4aN0 UC Clavian I (n/v)
micropapillary
features
75 Male 475 300 12 5 pT2 high grade UC pT2bN0, marg neg, pT2 None
adenocarcinoma of prostate,
ISUP grade 2
71 Female 420 100 18 5 pT1 high grade BCG pTisN0 UC, marg neg None
refractory
71 Male 425 750 8 5 pT1 high-grade, pT1N0, UC inside divertic, None
inside bladder margins neg
diverticulum
64 3 females, 387 117 11.9 5.4 2 T1; 10 T2 5
9 males
DISCUSSION
Urologists have always been early to adopt new technological advances in the field of surgery, and Urology
was one of the first subspecialties to widely adopt the use of the da Vinci robot for various procedures
involving the prostate, kidney, and bladder. Most notably, the use of the da Vinci robot has become so
widespread for radical prostatectomy that it is now used for up to 85% of all radical prostatectomies .
[8]
Urologists have been comparatively slower to adopt the robot for use in radical cystectomies, owing at least
in part to the cystectomy being a more complex and technically challenging procedure, particularly due to
the need for bladder reconstruction and urinary diversion. In addition, operative times tend to be longer for
the robotic cystectomy without current proven benefit in terms of local recurrence rates . There is relatively
[9]
little data currently out there on outcomes after SP RARC, owing in part to the newness of the SP system.
Nevertheless, the addition of the da Vinci SP platform represents an exciting advancement in the realm of
minimally invasive surgery, and with the rise in popularity and proven noninferiority of RARC compared to
ORC, it is worth exploring and reporting the feasibility, safety, and outcomes of RARC utilizing the SP
robot. The initial case reviews included in the study represent a promising start in demonstrating the safety
and feasibility of performing RARC using the da Vinci SP robot.
Conclusion
RARC with intracorporeal ileal conduit urinary diversion can be performed in a safe manner with good
preliminary outcomes using the new da Vinci SP platform. More studies with larger case volumes are
required to determine distinguishing variables such as average length of procedure, length of hospital stay,
complications, surgical margins, and post-operative local recurrence rates. Given numerous theoretical
benefits of the SP system over multiport, including improved cosmesis, reduced pain requirements, and
improved operative visualization in narrow spaces, it is an avenue of great interest in the field of minimally
invasive Urology and warrants further exploration.
DECLARATIONS
Authors’ contributions
Conceived the topic of study, provided guidance and expertise surrounding the technical steps of the
procedure, and critically revised the final manuscript: Crivellaro S