Page 10 - Read Online
P. 10
Page 4 of 11 Silvestri et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2019;3:5 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2018.67
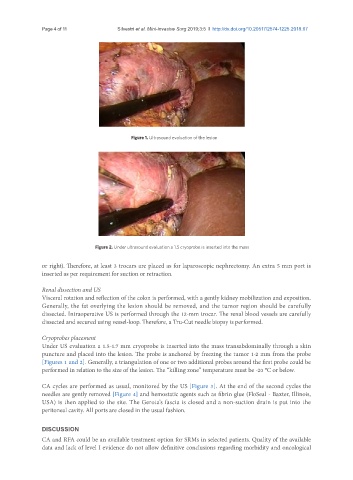
Figure 1. Ultrasound evaluation of the lesion
Figure 2. Under ultrasound evaluation a 1.5 cryoprobe is inserted into the mass
or right). Therefore, at least 3 trocars are placed as for laparoscopic nephrectomy. An extra 5 mm port is
inserted as per requirement for suction or retraction.
Renal dissection and US
Visceral rotation and reflection of the colon is performed, with a gently kidney mobilization and exposition.
Generally, the fat overlying the lesion should be removed, and the tumor region should be carefully
dissected. Intraoperative US is performed through the 12-mm trocar. The renal blood vessels are carefully
dissected and secured using vessel-loop. Therefore, a Tru-Cut needle biopsy is performed.
Cryoprobes placement
Under US evaluation a 1.5-1.7 mm cryoprobe is inserted into the mass transabdominally through a skin
puncture and placed into the lesion. The probe is anchored by freezing the tumor 1-2 mm from the probe
[Figures 1 and 2]. Generally, a triangulation of one or two additional probes around the first probe could be
performed in relation to the size of the lesion. The “killing zone” temperature must be -20 °C or below.
CA cycles are performed as usual, monitored by the US [Figure 3]. At the end of the second cycles the
needles are gently removed [Figure 4] and hemostatic agents such as fibrin glue (FloSeal - Baxter, Illinois,
USA) is then applied to the site. The Gerota’s fascia is closed and a non-suction drain is put into the
peritoneal cavity. All ports are closed in the usual fashion.
DISCUSSION
CA and RFA could be an available treatment option for SRMs in selected patients. Quality of the available
data and lack of level I evidence do not allow definitive conclusions regarding morbidity and oncological