Page 77 - Read Online
P. 77
Deivasigamani et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2023;7:9 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2022.99 Page 7 of 19
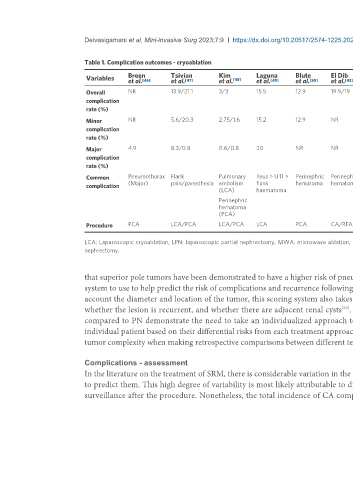
Table 1. Complication outcomes - cryoablation
Variables Breen Tsivian Kim [48] Laguna Blute El Dib Schmit Guazzoni Guillotreau Klatte Lucignani Cobelli Nielsen
et al.
et al.
et al.
et al.
et al.
et al.
et al.
et al.
et al.
et al.
et al.
et al.
et al.
[49]
[54]
[55]
[46]
[47]
[51]
[37]
[35]
[52]
[53]
[50]
[43]
Overall NR 13.9/21.1 3/3 15.5 12.9 19.9/19 NR 20.3 20/12 9.5/18 36.2/24 9.8/6.2 16.6%
complication
rate (%)
Minor NR 5.6/20.3 2.75/1.6 15.2 12.9 NR NR 17.8 17/8 NR 34.5/18.6 9/6.2 2.5%
complication
rate (%)
Major 4.9 8.3/0.8 0.6/0.8 20 NR NR 7.5% NR 6/8 NR 1.7/5.4 NR 3.2%
complication
rate (%)
Common Pneumothorax Flank Pulmonary Ileus > UTI > Perinephric Perinephric Hemorrhage Fever > NR hemorrhage Hemorrhage Hemorrhage hemorrhage
complication (Major) pain/paresthesia embolism flank hematoma hematoma hematoma effusion
(LCA) haematoma
Perinephric
hematoma
(PCA)
Procedure PCA LCA/PCA LCA/PCA LCA PCA CA/RFA PCA LCA RPN/LCA LCA/L(R)PN CA/MWA CA/MWA LCA
LCA: Laparoscopic cryoablation; LPN: laparoscopic partial nephrectomy; MWA: microwave ablation; NR: not reported; PCA: percutaneous cryoablation; RFA: radiofrequency ablation; RPN: robotic partial
nephrectomy.
that superior pole tumors have been demonstrated to have a higher risk of pneumothorax . More recently, the ABLATE score has been proposed as a scoring
[46]
system to use to help predict the risk of complications and recurrence following percutaneous ablation treatment of renal lesions, and in addition to taking into
account the diameter and location of the tumor, this scoring system also takes into account proximity of other organs, the angle of the tumor on the kidney,
whether the lesion is recurrent, and whether there are adjacent renal cysts . The differences in what factors affect the risk of complication following PCA
[59]
compared to PN demonstrate the need to take an individualized approach to patient care to determine the management option that would best suit the
individual patient based on their differential risks from each treatment approach. These differences also highlight the problem with attempts at controlling for
tumor complexity when making retrospective comparisons between different techniques for treating renal masses.
Complications - assessment
In the literature on the treatment of SRM, there is considerable variation in the reported rates of complications, their classification systems, and the scores used
to predict them. This high degree of variability is most likely attributable to differences in baseline patient characteristics, the expertise of the provider, and
surveillance after the procedure. Nonetheless, the total incidence of CA complications appears to be quite low, with the great majority minor in nature as