Page 26 - Read Online
P. 26
Chu et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2022;6:290-303 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2022.02 Page 292
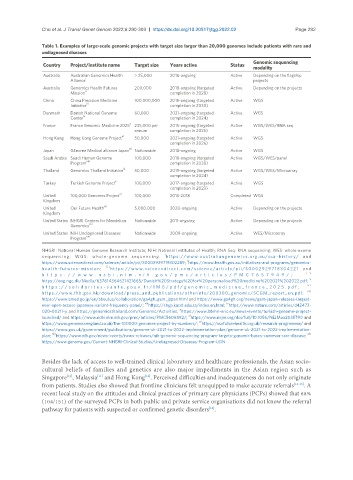
Table 1. Examples of large-scale genomic projects with target size larger than 20,000 genomes include patients with rare and
undiagnosed diseases
Genomic sequencing
Country Project/institute name Target size Years active Status
modality
Australia Australian Genomics Health > 25,000 2016-ongoing Active Depending on the flagship
Alliance i projects
Australia Genomics Health Futures 200,000 2018-ongoing (targeted Active Depending on the projects
ii
Mission completion in 2028)
China China Precision Medicine 100,000,000 2015-ongoing (targeted Active WGS
iii
Initiative completion in 2030)
Denmark Danish National Genome 60,000 2021-ongoing (targeted Active WGS
iv
Center completion in 2024)
France France Genomic Medicine 2025 v 235,000 per 2015-ongoing (targeted Active WGS/WES/RNA seq
annum completion in 2025)
Hong Kong Hong Kong Genome Project vi 50,000 2021-ongoing (targeted Active WGS
completion in 2026)
Japan GEnome Medical alliance Japan vii Nationwide 2018-ongoing Active WGS
Saudi Arabia Saudi Human Genome 100,000 2018-ongoing (targeted Active WGS/WES/panel
viii
Program completion in 2030)
ix
Thailand Genomics Thailand Initiative 50,000 2019-ongoing (targeted Active WGS/WES/Microarray
completion in 2024)
Turkey Turkish Genome Project x 100,000 2017-ongoing (targeted Active WGS
completion in 2023)
United 100,000 Genomes Project xi 100,000 2013-2018 Completed WGS
Kingdom
United Our Future Health xii 5,000,000 2020-ongoing Active Depending on the projects
Kingdom
United States NHGRI Centers for Mendelian Nationwide 2011-ongoing Active Depending on the projects
xiii
Genomics
United States NIH Undiagnosed Diseases Nationwide 2008-ongoing Active WES/Microarray
xiv
Program
NHGRI: National Human Genome Research Institute; NIH: National Institutes of Health; RNA Seq: RNA sequencing; WES: whole-exome
i
s e q u e n c i n g ; W G S : w h o l e - g e n o m e s e q u e n c i n g . h t t p s : / / w w w . a u s t r a l i a n g e n o m i c s . o r g . a u / o u r - h i s t o r y / a n d
ii
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0002929719302289; https://www.health.gov.au/initiatives-and-programs/genomics-
h e a l t h - f u t u r e s - m i s s i o n ; i i i h t t p s : / / w w w . s c i e n c e d i r e c t . c o m / s c i e n c e / a r t i c l e / p i i / S 0 0 0 2 9 2 9 7 1 8 3 0 4 2 2 1 a n d
h t t p s : / / w w w . n c b i . n l m . n i h . g o v / p m c / a r t i c l e s / P M C 7 6 5 7 9 4 9 / ; i v
v
https://eng.ngc.dk/Media/637614364621421665/Danish%20Strategy%20for%20personalised%20medicine%202021%202022.pdf;
v i
h t t p s : / / s o l i d a r i t e s - s a n t e . g o u v . f r / I M G / p d f / g e n o m i c _ m e d i c i n e _ f r a n c e _ 2 0 2 5 . p d f ;
https://www.fhb.gov.hk/download/press_and_publications/otherinfo/200300_genomic/SCGM_report_en.pdf; vii
https://www.amed.go.jp/en/aboutus/collaboration/ga4gh_gem_japan.html and https://www.ga4gh.org/news/gem-japan-releases-largest-
viii ix
ever-open-access-japanese-variant-frequency-panel/; https://shgp.kacst.edu.sa/index.en.html; https://www.nature.com/articles/d42473-
x
020-00211-y and https://genomicsthailand.com/Genomic/Activities; https://www.bbmri-eric.eu/news-events/turkish-genome-project-
xi
launched/ and https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5606892/; https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2035790 and
xii
https://www.genomicsengland.co.uk/the-100000-genomes-project-by-numbers/; https://ourfuturehealth.org.uk/research-programme/ and
https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/genome-uk-2021-to-2022-implementation-plan/genome-uk-2021-to-2022-implementation-
xiii xiv
plan; https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/nih-genome-sequencing-program-targets-genomic-bases-common-rare-disease;
https://www.genome.gov/Current-NHGRI-Clinical-Studies/Undiagnosed-Diseases-Program-UDN
Besides the lack of access to well-trained clinical laboratory and healthcare professionals, the Asian socio-
cultural beliefs of families and genetics are also major impediments in the Asian region such as
[10]
[11]
[12]
Singapore , Malaysia and Hong Kong . Perceived difficulties and inadequateness do not only originate
from patients. Studies also showed that frontline clinicians felt unequipped to make accurate referrals [13-15] . A
recent local study on the attitudes and clinical practices of primary care physicians (PCPs) showed that 68%
(104/151) of the surveyed PCPs in both public and private service organisations did not know the referral
pathway for patients with suspected or confirmed genetic disorders .
[16]