Page 11 - Read Online
P. 11
Page 83 Cox et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2021;5:80-8 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2021.06
Table 1. Summary of omic analyses in chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy
Sequencing type Sample Conclusion Ref.
RNA sequencing CART Non-responders - exhausted CD8 phenotype [22]
Responders - memory phenotype
Whole exome sequencing ± CNV Tumor Classification genetic subtypes of DLBCL [23]
TCRB sequencing, lentiviral integration site CART Some clones have a better survival capability [24]
analysis
RNA sequencing
Lentiviral integration site analysis CART Lentiviruses preferentially incorporate into accessible chromatin [26]
ATAC sequencing AP-1 family is associated with activation and expansion
Single cell RNA, sequencing CART Monocyte-like gene expression signature associated with high-grade [22]
neurotoxicity
RNA sequencing Brain A subset of mural cells expresses CD19 [30]
tissue
RNA sequencing TME Monocytes acquire unique gene expression in the TME [33]
RNA sequencing nanostring TME Lower T-cell-related genes and higher macrophage-related genes associated [34]
with neurotoxicity
Single cell RNA sequencing TME Upregulated PD-L1 in murine and human tumor [36]
TCRB sequencing TME Specific clones of T cells survive better than others [37]
Whole genome sequencing Tumor Mechanism of antigen escape in occurs in exon 2 of CD19 and is regulated by [41]
RNA sequencing SRSF3 splice factor
sgRNA sequencing Tumor Death receptor signature can predict response [43]
RNA: Ribonucleic acid; CNV: copy number variant; ATAC: assay for transposase-accessible chromatin; sgRNA: single guide RNA; CART: chimeric
antigen receptor T cell; TME: tumor microenvironment; DLBCL: diffuse large B cell lymphoma; TCRB: T cell receptor beta; PD-L1: programmed
death ligand 1; SRSF3: serine and arginine rich splicing factor 3.
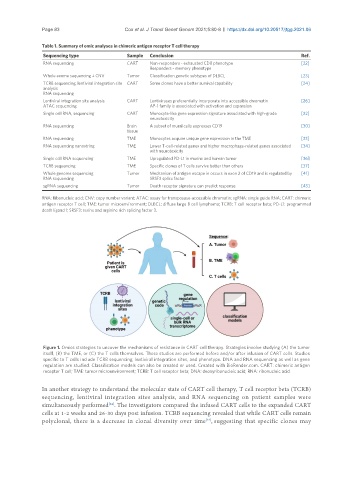
Figure 1. Omics strategies to uncover the mechanisms of resistance in CART cell therapy. Strategies involve studying (A) the tumor
itself, (B) the TME, or (C) the T cells themselves. These studies are performed before and/or after infusion of CART cells. Studies
specific to T cells include TCRB sequencing, lentiviral integration sites, and phenotype. DNA and RNA sequencing as well as gene
regulation are studied. Classification models can also be created or used. Created with BioRender.com. CART: chimeric antigen
receptor T cell; TME: tumor microenvironment; TCRB: T cell receptor beta; DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid; RNA: ribonucleic acid.
In another strategy to understand the molecular state of CART cell therapy, T cell receptor beta (TCRB)
sequencing, lentiviral integration sites analysis, and RNA sequencing on patient samples were
simultaneously performed . The investigators compared the infused CART cells to the expanded CART
[24]
cells at 1-2 weeks and 26-30 days post infusion. TCRB sequencing revealed that while CART cells remain
[24]
polyclonal, there is a decrease in clonal diversity over time , suggesting that specific clones may