Page 25 - Read Online
P. 25
Page 24 Berardo et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2020;4:22-35 I https://doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2020.02
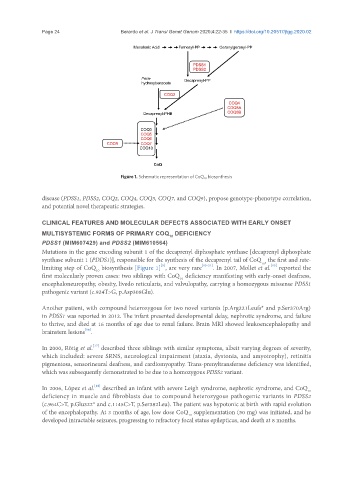
Figure 1. Schematic representation of CoQ 10 biosynthesis
disease (PDSS1, PDSS2, COQ2, COQ4, COQ5, COQ7, and COQ9), propose genotype-phenotype correlation,
and potential novel therapeutic strategies.
CLINICAL FEATURES AND MOLECULAR DEFECTS ASSOCIATED WITH EARLY ONSET
MULTISYSTEMIC FORMS OF PRIMARY COQ DEFICIENCY
10
PDSS1 (MIM607429) and PDSS2 (MIM610564)
Mutations in the gene encoding subunit 1 of the decaprenyl diphosphate synthase [decaprenyl diphosphate
synthase subunit 1 (PDDS1)], responsible for the synthesis of the decaprenyl tail of CoQ , the first and rate-
10
[5]
[15]
limiting step of CoQ biosynthesis [Figure 1] , are very rare [15-21] . In 2007, Mollet et al. reported the
10
first molecularly proven cases: two siblings with CoQ deficiency manifesting with early-onset deafness,
10
encephaloneuropathy, obesity, livedo reticularis, and valvulopathy, carrying a homozygous missense PDSS1
pathogenic variant (c.924T>G, p.Asp308Glu).
Another patient, with compound heterozygous for two novel variants (p.Arg221Leufs* and p.Ser370Arg)
in PDSS1 was reported in 2012. The infant presented developmental delay, nephrotic syndrome, and failure
to thrive, and died at 16 months of age due to renal failure. Brain MRI showed leukoencephalopathy and
[16]
brainstem lesions .
[17]
In 2000, Rötig et al. described three siblings with similar symptoms, albeit varying degrees of severity,
which included: severe SRNS, neurological impairment (ataxia, dystonia, and amyotrophy), retinitis
pigmentosa, sensorineural deafness, and cardiomyopathy. Trans-prenyltransferase deficiency was identified,
which was subsequently demonstrated to be due to a homozygous PDSS2 variant.
In 2006, López et al. described an infant with severe Leigh syndrome, nephrotic syndrome, and CoQ
[18]
10
deficiency in muscle and fibroblasts due to compound heterozygous pathogenic variants in PDSS2
(c.964C>T, p.Glu322* and c.1145C>T, p.Ser382Leu). The patient was hypotonic at birth with rapid evolution
of the encephalopathy. At 3 months of age, low dose CoQ supplementation (50 mg) was initiated, and he
10
developed intractable seizures, progressing to refractory focal status epilepticus, and death at 8 months.