Page 59 - Read Online
P. 59
Bibi et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2024;8:119-161 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2023.50 Page 149
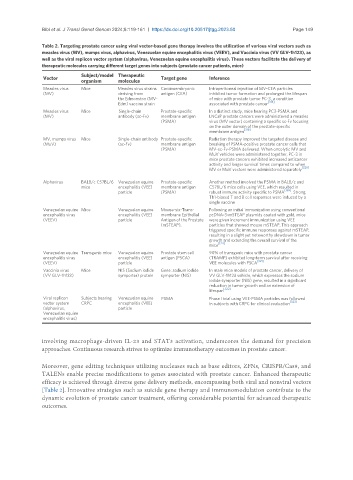
Table 2. Targeting prostate cancer using viral vector-based gene therapy involves the utilization of various viral vectors such as
measles virus (MV), mumps virus, alphavirus, Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus (VEEV), and Vaccinia virus (VV GLV-1h123), as
well as the viral replicon vector system (alphavirus, Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus). These vectors facilitate the delivery of
therapeutic molecules carrying different target genes into subjects (prostate cancer patients, mice)
Vector Subject/model Therapeutic Target gene Inference
organism molecules
Measles virus Mice Measles virus strains Carcinoembryonic Intraperitoneal injection of MV-CEA particles
(MV) deriving from antigen (CEA) inhibited tumor formation and prolonged the lifespan
the Edmonston (MV- of mice with prostate tumor PC-3, a condition
[318]
Edm) vaccine strain associated with prostate cancer
Measles virus Mice Single-chain Prostate-specific In a distinct study, mice bearing PC3-PSMA and
(MV) antibody (sc-Fv) membrane antigen LNCaP prostate cancers were administered a measles
(PSMA) virus (MV vector) containing a specific sc-Fv focusing
on the outer domain of the prostate-specific
membrane antigen [319]
MV, mumps virus Mice Single-chain antibody Prostate-specific Radiation therapy improved the targeted disease and
(MuV) (sc-Fv) membrane antigen breaking of PSMA-positive prostate cancer cells that
(PSMA) MV-sc-Fv-PSMA delivered. When oncolytic MV and
MuV vehicles were administered together, PC-3 in
mice prostate cancers exhibited increased anticancer
activity and longer survival times compared to when
MV or MuV vectors were administered separately [320]
Alphavirus BALB/c C57BL/6 Venezuelan equine Prostate-specific Another method involved the PSMA in BALB/c and
mice encephalitis (VEE) membrane antigen C57BL/6 mice cells using VEE, which resulted in
particle (PSMA) robust immune activity specific to PSMA [169] . Strong,
Th1-biased T and B cell responses were induced by a
single vaccine
Venezuelan equine Mice Venezuelan equine Mouse-six-Trans- Following an initial immunization using conventional
encephalitis virus encephalitis (VEE) membrane Epithelial pcDNA-3-mSTEAP plasmids coated with gold, mice
(VEEV) particle Antigen of the Prostate were given increment immunization using VEE
(mSTEAP). particles that showed mouse mSTEAP. This approach
triggered specific immune responses against mSTEAP,
resulting in a slight yet noteworthy slowdown in tumor
growth and extending the overall survival of the
[124]
mice
Venezuelan equine Transgenic mice Venezuelan equine Prostate stem cell 90% of transgenic mice with prostate cancer
encephalitis virus encephalitis (VEE) antigen (PSCA) (TRAMP) exhibited long-term survival after receiving
(VEEV) particle VEE molecules with PSCA [321]
Vaccinia virus Mice NIS (Sodium iodide Gene: sodium iodide In male mice models of prostate cancer, delivery of
(VV GLV-1h123) symporter) protein symporter (NIS) VV GLV-1h123 vehicle, which expresses the sodium
iodide symporter (NIS) gene, resulted in a significant
reduction in tumor growth and an extension of
lifespan [322]
Viral replicon Subjects bearing Venezuelan equine PSMA Phase I trial using VEE-PSMA particles was followed
vector system CRPC encephalitis (VEE) in subjects with CRPC for clinical evaluation [323]
(alphavirus, particle
Venezuelan equine
encephalitis virus)
involving macrophage-driven IL-23 and STAT3 activation, underscores the demand for precision
approaches. Continuous research strives to optimize immunotherapy outcomes in prostate cancer.
Moreover, gene editing techniques utilizing nucleases such as base editors, ZFNs, CRISPR/Cas9, and
TALENs enable precise modifications to genes associated with prostate cancer. Enhanced therapeutic
efficacy is achieved through diverse gene delivery methods, encompassing both viral and nonviral vectors
[Table 2]. Innovative strategies such as suicide gene therapy and immunomodulation contribute to the
dynamic evolution of prostate cancer treatment, offering considerable potential for advanced therapeutic
outcomes.