Page 108 - Read Online
P. 108
Page 69 Oboma et al. J Transl Genet Genom. 2025;9:62-75 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2024.74
[18]
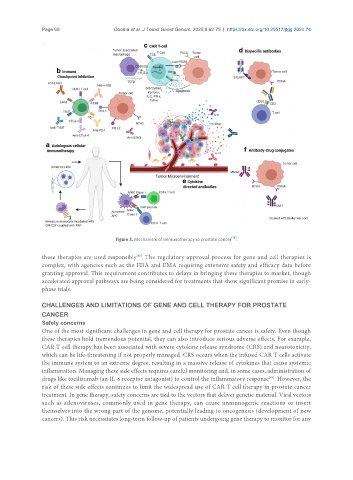
Figure 3. Mechanism of Immunotherapy in prostate cancer .
these therapies are used responsibly . The regulatory approval process for gene and cell therapies is
[50]
complex, with agencies such as the FDA and EMA requiring extensive safety and efficacy data before
granting approval. This requirement contributes to delays in bringing these therapies to market, though
accelerated approval pathways are being considered for treatments that show significant promise in early-
phase trials.
CHALLENGES AND LIMITATIONS OF GENE AND CELL THERAPY FOR PROSTATE
CANCER
Safety concerns
One of the most significant challenges in gene and cell therapy for prostate cancer is safety. Even though
these therapies hold tremendous potential, they can also introduce serious adverse effects. For example,
CAR T cell therapy has been associated with severe cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity,
which can be life-threatening if not properly managed. CRS occurs when the infused CAR T cells activate
the immune system to an extreme degree, resulting in a massive release of cytokines that cause systemic
inflammation. Managing these side effects requires careful monitoring and, in some cases, administration of
drugs like tocilizumab (an IL-6 receptor antagonist) to control the inflammatory response . However, the
[48]
risk of these side effects continues to limit the widespread use of CAR T cell therapy in prostate cancer
treatment. In gene therapy, safety concerns are tied to the vectors that deliver genetic material. Viral vectors
such as adenoviruses, commonly used in gene therapy, can cause immunogenic reactions or insert
themselves into the wrong part of the genome, potentially leading to oncogenesis (development of new
cancers). This risk necessitates long-term follow-up of patients undergoing gene therapy to monitor for any