Page 73 - Read Online
P. 73
Page 66 Jiang et al. J Surveill Secur Saf 2020;1:61-78 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jsss.2020.09
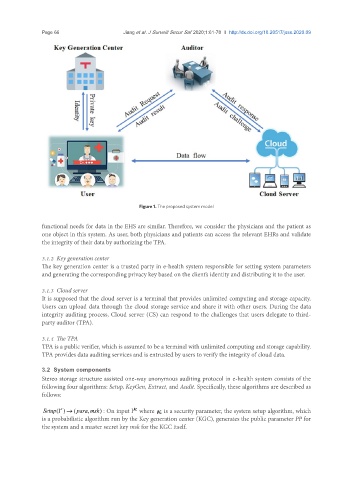
Figure 1. The proposed system model
functional needs for data in the EHS are similar. Therefore, we consider the physicians and the patient as
one object in this system. As user, both physicians and patients can access the relevant EHRs and validate
the integrity of their data by authorizing the TPA.
3.1.2 Key generation center
The key generation center is a trusted party in e-health system responsible for setting system parameters
and generating the corresponding privacy key based on the client’s identity and distributing it to the user.
3.1.3 Cloud server
It is supposed that the cloud server is a terminal that provides unlimited computing and storage capacity.
Users can upload data through the cloud storage service and share it with other users. During the data
integrity auditing process, Cloud server (CS) can respond to the challenges that users delegate to third-
party auditor (TPA).
3.1.4 The TPA
TPA is a public verifier, which is assumed to be a terminal with unlimited computing and storage capability.
TPA provides data auditing services and is entrusted by users to verify the integrity of cloud data.
3.2 System components
Stereo storage structure assisted one-way anonymous auditing protocol in e-health system consists of the
following four algorithms: Setup, KeyGen, Extract, and Audit. Specifically, these algorithms are described as
follows:
(
,
κ
)
Setup (1 ) → para msk : On input l where is a security parameter, the system setup algorithm, which
is a probabilistic algorithm run by the Key generation center (KGC), generates the public parameter PP for
the system and a master secret key msk for the KGC itself.