Page 63 - Read Online
P. 63
Page 56 Kim et al. J Surveill Secur Saf 2020;1:34-60 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jsss.2020.14
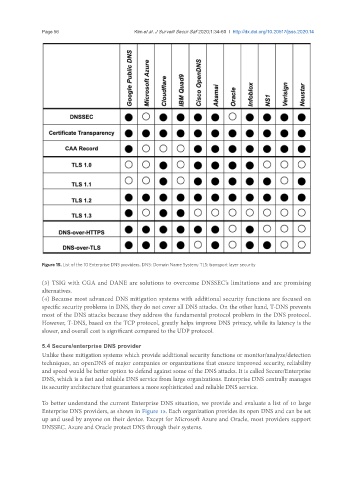
Figure 15. List of the 10 Enterprise DNS providers. DNS: Domain Name System; TLS: transport layer security
(3) TSIG with CGA and DANE are solutions to overcome DNSSEC’s limitations and are promising
alternatives.
(4) Because most advanced DNS mitigation systems with additional security functions are focused on
specific security problems in DNS, they do not cover all DNS attacks. On the other hand, T-DNS prevents
most of the DNS attacks because they address the fundamental protocol problem in the DNS protocol.
However, T-DNS, based on the TCP protocol, greatly helps improve DNS privacy, while its latency is the
slower, and overall cost is significant compared to the UDP protocol.
5.4 Secure/enterprise DNS provider
Unlike these mitigation systems which provide additional security functions or monitor/analyze/detection
techniques, an openDNS of major companies or organizations that ensure improved security, reliability
and speed would be better option to defend against some of the DNS attacks. It is called Secure/Enterprise
DNS, which is a fast and reliable DNS service from large organizations. Enterprise DNS centrally manages
its security architecture that guarantees a more sophisticated and reliable DNS service.
To better understand the current Enterprise DNS situation, we provide and evaluate a list of 10 large
Enterprise DNS providers, as shown in Figure 15. Each organization provides its open DNS and can be set
up and used by anyone on their device. Except for Microsoft Azure and Oracle, most providers support
DNSSEC. Azure and Oracle protect DNS through their systems.