Page 126 - Read Online
P. 126
Page 6 of 19 Chen et al. J Mater Inf 2023;3:10 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jmi.2023.06
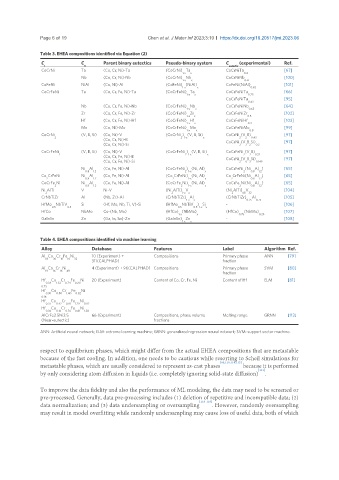
Table 3. EHEA compositions identified via Equation (2)
C C Parent binary eutectics Pseudo-binary system C (experimental) Ref.
I II eutectic
CoCrNi Ta (Co, Cr, Ni)-Ta (CoCrNi) Ta CoCrNiTa [67]
1-x x 0.4
Nb (Co, Cr, Ni)-Nb (CoCrNi) Nb CoCrNiNb [100]
1-x x 0.4
CoFeNi NiAl (Co, Ni)-Al (CoFeNi) (NiAl) CoFeNi(NiAl) [101]
1-x x 0.92
CoCrFeNi Ta (Co, Cr, Fe, Ni)-Ta (CoCrFeNi) Ta CoCrFeNiTa [66]
1-x x 0.75
CoCrFeNiTa [95]
0.43
Nb (Co, Cr, Fe, Ni)-Nb (CoCrFeNi) Nb CoCrFeNiNb [64]
1-x x 0.65
Zr (Co, Cr, Fe, Ni)-Zr (CoCrFeNi) Zr CoCrFeNiZr [102]
1-x x 0.5
Hf (Co, Cr, Fe, Ni)-Hf (CoCrFeNi) Hf CoCrFeNiHf [103]
1-x x 0.4
Mo (Co, Ni)-Mo (CoCrFeNi) Mo CoCrFeNiMo [99]
1-x x 0.8
CoCrNi (V, B, Si) (Co, Ni)-V (CoCrNi ) (V, B, Si) CoCrNi (V B) [97]
2 2 1-x x 2 2 0.43
(Co, Cr, Ni)-B CoCrNi (V B Si) [97]
(Co, Cr, Ni)-Si 2 3 2 0.2
CoCrFeNi (V, B, Si) (Co, Ni)-V (CoCrFeNi ) (V, B, Si) CoCrFeNi (V B) [97]
2 2 1-x x 2 2 0.51
(Co, Cr, Fe, Ni)-B CoCrNi (V B Si) [97]
(Co, Cr, Fe, Ni)-Si 2 6 3 0.149
Ni Al (Co, Fe, Ni)-Al (CoCrFeNi ) (Ni, Al) CoCrFeNi (Ni Al ) [65]
0.8 1.2 2 1-x x 2 0.8 1.2
Co CrFeNi Ni Al (Co, Fe, Ni)-Al (Co CrFeNi) (Ni, Al) Co CrFeNi(Ni Al ) [65]
2 0.8 1.2 2 1-x x 2 0.8 1.2
CoCrFe Ni Ni Al (Co, Fe, Ni)-Al (CoCrFe Ni) (Ni, Al) CoCrFe Ni(Ni Al ) [65]
2 0.8 1.2 2 1-x x 2 0.8 1.2
Ni AlTi V Ni-V (Ni AlTi) V (Ni AlTi) V [104]
2 2 1-x x 2 68 32
CrNbTiZr Al (Nb, Zr)-Al (CrNbTiZr) Al (CrNbTiZr) Al [105]
1-x x 0.25 0.75
HfMo NbTiV Si (Hf, Mo, Nb, Ti, V)-Si (HfMo NbTiV ) Si - [106]
0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 1-x x
HfCo NbMo Co-(Nb, Mo) (HfCo) (NbMo) (HfCo) (NbMo) [107]
1-x x 0.75 0.25
GaInSn Zn (Ga, In, Sn)-Zn (GaInSn) Zn - [108]
1-x x
Table 4. EHEA compositions identified via machine learning
Alloy Database Features Label Algorithm Ref.
Al Co Cr Fe Ni 10 (Experiment) + Compositions Primary phase ANN [79]
18 30 10 10 32
311(CALPHAD) fraction
Al Co Cr Ni 4 (Experiment) + 96(CALPHAD) Compositions Primary phase SVM [80]
19 16 16 49
fraction
Hf Co Cr Fe Ni 20 (Experiment) Content of Co, Cr, Fe, Ni Content of Hf ELM [81]
0.34 1.33 0.74 0.20
0.75
Hf Co Cr Fe Ni
0.30 0.80 1.40 0.82
0.16
Hf Co Cr Fe Ni
0.37 0.42 0.81 1.29 0.82
Hf Co Cr Fe Ni
0.36 0.16 0.76 0.81 1.38
AlCrFe2.5Ni2.5 66 (Experiment) Compositions, phase volume Melting range GRNN [113]
(Near-eutectic) fractions
ANN: Artificial neural network; ELM: extreme learning machine; GRNN: generalized regression neural network; SVM: support vector machine.
respect to equilibrium phases, which might differ from the actual EHEA compositions that are metastable
because of the fast cooling. In addition, one needs to be cautious while resorting to Scheil simulations for
[63,110,114,115]
metastable phases, which are usually considered to represent as-cast phases because it is performed
[111]
by only considering atom diffusion in liquids (i.e. completely ignoring solid-state diffusion) .
To improve the data fidelity and also the performance of ML modeling, the data may need to be screened or
pre-processed. Generally, data pre-processing includes (1) deletion of repetitive and incompatible data; (2)
data normalization; and (3) data undersampling or oversampling [116-118] . However, randomly oversampling
may result in model overfitting while randomly undersampling may cause loss of useful data, both of which