Page 567 - Read Online
P. 567
Cordover et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:45 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.101 Page 3 of 19
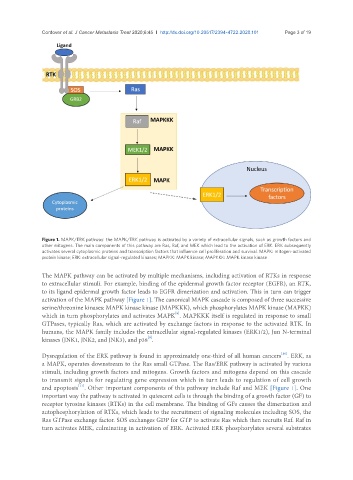
Figure 1. MAPK/ERK pathway: the MAPK/ERK pathway is activated by a variety of extracellular signals, such as growth factors and
other mitogens. The main components of this pathway are Ras, Raf, and MEK which lead to the activation of ERK. ERK subsequently
activates several cytoplasmic proteins and transcription factors that influence cell proliferation and survival. MAPK: mitogen-activated
protein kinase; ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinases; MAPKK: MAPK kinase; MAPKKK: MAPK kinase kinase
The MAPK pathway can be activated by multiple mechanisms, including activation of RTKs in response
to extracellular stimuli. For example, binding of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), an RTK,
to its ligand epidermal growth factor leads to EGFR dimerization and activation. This in turn can trigger
activation of the MAPK pathway [Figure 1]. The canonical MAPK cascade is composed of three successive
serine/threonine kinases: MAPK kinase kinase (MAPKKK), which phosphorylates MAPK kinase (MAPKK)
[8]
which in turn phosphorylates and activates MAPK . MAPKKK itself is regulated in response to small
GTPases, typically Ras, which are activated by exchange factors in response to the activated RTK. In
humans, the MAPK family includes the extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK1/2), Jun N-terminal
[9]
kinases (JNK1, JNK2, and JNK3), and p38 .
[10]
Dysregulation of the ERK pathway is found in approximately one-third of all human cancers . ERK, as
a MAPK, operates downstream to the Ras small GTPase. The Ras/ERK pathway is activated by various
stimuli, including growth factors and mitogens. Growth factors and mitogens depend on this cascade
to transmit signals for regulating gene expression which in turn leads to regulation of cell growth
and apoptosis . Other important components of this pathway include Raf and MEK [Figure 1]. One
[11]
important way the pathway is activated in quiescent cells is through the binding of a growth factor (GF) to
receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) in the cell membrane. The binding of GFs causes the dimerization and
autophosphorylation of RTKs, which leads to the recruitment of signaling molecules including SOS, the
Ras GTPase exchange factor. SOS exchanges GDP for GTP to activate Ras which then recruits Raf. Raf in
turn activates MEK, culminating in activation of ERK. Activated ERK phosphorylates several substrates