Page 350 - Read Online
P. 350
dos Santos et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:25 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.83 Page 13 of 20
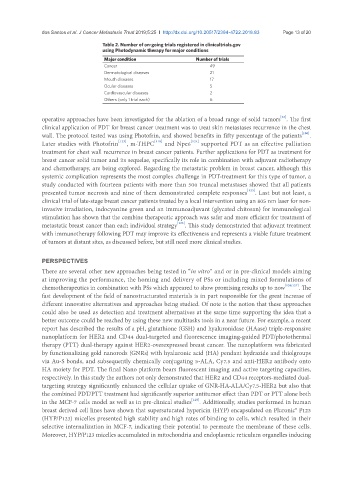
Table 2. Number of on-going trials registered in clinicaltrials.gov
using Photodynamic therapy for major conditions
Major condition Number of trials
Cancer 49
Dermatological diseases 21
Mouth diseases 17
Ocular diseases 5
Cardiovascular diseases 2
Others (only 1 trial each) 6
[22]
operative approaches have been investigated for the ablation of a broad range of solid tumors . The first
clinical application of PDT for breast cancer treatment was to treat skin metastases recurrence in the chest
wall. The protocol tested was using Photofrin, and showed benefits in fifty percentage of the patients [100] .
Later studies with Photofrin [123] , m-THPC [119] and Npe6 [124] supported PDT as an effective palliation
treatment for chest wall recurrence in breast cancer patients. Further applications for PDT as treatment for
breast cancer solid tumor and its sequelae, specifically its role in combination with adjuvant radiotherapy
and chemotherapy, are being explored. Regarding the metastatic problem in breast cancer, although this
systemic complication represents the most complex challenge in PDT-treatment for this type of tumor, a
study conducted with fourteen patients with more than 500 truncal metastases showed that all patients
presented tumor necrosis and nine of them demonstrated complete responses [123] . Last but not least, a
clinical trial of late-stage breast cancer patients treated by a local intervention using an 805 nm laser for non-
invasive irradiation, indocyanine green and an immunoadjuvant (glycated chitosan) for immunological
stimulation has shown that the combine therapeutic approach was safer and more efficient for treatment of
metastatic breast cancer than each individual strategy [125] . This study demonstrated that adjuvant treatment
with immunotherapy following PDT may improve its effectiveness and represents a viable future treatment
of tumors at distant sites, as discussed before, but still need more clinical studies.
PERSPECTIVES
There are several other new approaches being tested in “in vitro” and or in pre-clinical models aiming
at improving the performance, the homing and delivery of PSs or including mixed formulations of
chemotherapeutics in combination with PSs which appeared to show promising results up to now [126,127] . The
fast development of the field of nanostructurated materials is in part responsible for the great increase of
different innovative alternatives and approaches being studied. Of note is the notion that these approaches
could also be used as detection and treatment alternatives at the same time supporting the idea that a
better outcome could be reached by using these new multitasks tools in a near future. For example, a recent
report has described the results of a pH, glutathione (GSH) and hyaluronidase (HAase) triple-responsive
nanoplatform for HER2 and CD44 dual-targeted and fluorescence imaging-guided PDT/photothermal
therapy (PTT) dual-therapy against HER2-overexpressed breast cancer. The nanoplatform was fabricated
by functionalizing gold nanorods (GNRs) with hyaluronic acid (HA) pendant hydrazide and thiolgroups
via Au-S bonds, and subsequently chemically conjugating 5-ALA, Cy7.5 and anti-HER2 antibody onto
HA moiety for PDT. The final Nano platform bears fluorescent imaging and active targeting capacities,
respectively. In this study the authors not only demonstrated that HER2 and CD44 receptors-mediated dual-
targeting strategy significantly enhanced the cellular uptake of GNR-HA-ALA/Cy7.5-HER2 but also that
the combined PDT/PTT treatment had significantly superior antitumor effect than PDT or PTT alone both
in the MCF-7 cells model as well as in pre-clinical studies [128] . Additionally, studies performed in human
breast derived cell lines have shown that supersaturated hypericin (HYP) encapsulated on Pluronic® P123
(HYP/P123) micelles presented high stability and high rates of binding to cells, which resulted in their
selective internalization in MCF-7, indicating their potential to permeate the membrane of these cells.
Moreover, HYP/P123 micelles accumulated in mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum organelles inducing