Page 35 - Read Online
P. 35
ALHulais et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:3 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.71 Page 5 of 23
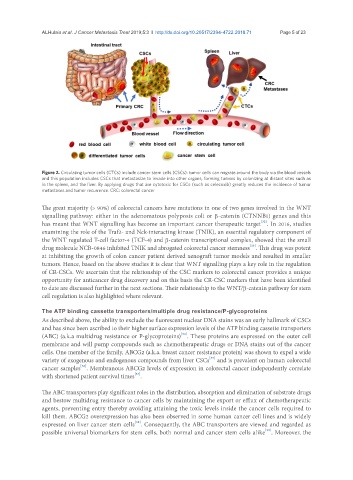
Figure 2. Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) include cancer stem cells (CSCs): tumor cells can migrate around the body via the blood vessels
and this population includes CSCs that metastasize to invade into other organs, forming tumors by colonizing at distant sites such as
in the spleen, and the liver. By applying drugs that are cytotoxic for CSCs (such as celecoxib) greatly reduces the incidence of tumor
metastases and tumor recurrence. CRC: colorectal cancer
The great majority (> 90%) of colorectal cancers have mutations in one of two genes involved in the WNT
signalling pathway: either in the adenomatous polyposis coli or b-catenin (CTNNB1) genes and this
[32]
has meant that WNT signalling has become an important cancer therapeutic target . In 2016, studies
examining the role of the Traf2- and Nck-interacting kinase (TNIK), an essential regulatory component of
the WNT regulated T-cell factor-4 (TCF-4) and b-catenin transcriptional complex, showed that the small
[33]
drug molecule NCB-0846 inhibited TNIK and abrogated colorectal cancer stemness . This drug was potent
at inhibiting the growth of colon cancer patient derived xenograft tumor models and resulted in smaller
tumors. Hence, based on the above studies it is clear that WNT signalling plays a key role in the regulation
of CR-CSCs. We ascertain that the relationship of the CSC markers to colorectal cancer provides a unique
opportunity for anticancer drug discovery and on this basis the CR-CSC markers that have been identified
to date are discussed further in the next sections. Their relationship to the WNT/b-catenin pathway for stem
cell regulation is also highlighted where relevant.
The ATP binding cassette transporters/multiple drug resistance/P-glycoproteins
As described above, the ability to exclude the fluorescent nuclear DNA stains was an early hallmark of CSCs
and has since been ascribed to their higher surface expression levels of the ATP binding cassette transporters
[34]
(ABC) (a.k.a multidrug resistance or P-glycoproteins) . These proteins are expressed on the outer cell
membrane and will pump compounds such as chemotherapeutic drugs or DNA stains out of the cancer
cells. One member of the family, ABCG2 (a.k.a. breast cancer resistance protein) was shown to expel a wide
[35]
variety of exogenous and endogenous compounds from liver CSCs and is prevalent on human colorectal
[36]
cancer samples . Membranous ABCG2 levels of expression in colorectal cancer independently correlate
[37]
with shortened patient survival times .
The ABC transporters play significant roles in the distribution, absorption and elimination of substrate drugs
and bestow multidrug resistance to cancer cells by maintaining the export or efflux of chemotherapeutic
agents, preventing entry thereby avoiding attaining the toxic levels inside the cancer cells required to
kill them. ABCG2 overexpression has also been observed in some human cancer cell lines and is widely
[38]
expressed on liver cancer stem cells . Consequently, the ABC transporters are viewed and regarded as
[39]
possible universal biomarkers for stem cells, both normal and cancer stem cells alike . Moreover, the