Page 58 - Read Online
P. 58
Torres et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2018;4:4 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2017.49 Page 5 of 25
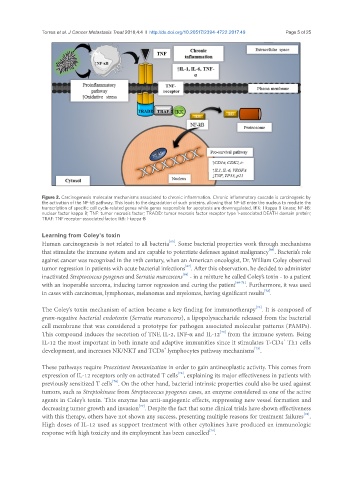
Figure 2. Carcinogenesis molecular mechanisms associated to chronic inflammation. Chronic inflammatory cascade is carcinogenic by
the activation of the NF-kB pathway. This leads to the degradation of such proteins, allowing that NF-kB enter the nucleus to mediate the
transcription of specific cell cycle-related genes while genes responsible for apoptosis are downregulated. IKK: I kappa B kinase; NF-kB:
nuclear factor kappa B; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; TRADD: tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1-associated DEATH domain protein;
TRAF: TNF receptor-associated factor; IkB: I-kappa-B
Learning from Coley’s toxin
[65]
Human carcinogenesis is not related to all bacteria . Some bacterial properties work through mechanisms
[66]
that stimulate the immune system and are capable to potentiate defenses against malignancy . Bacteria’s role
against cancer was recognized in the 19th century, when an American oncologist, Dr. William Coley observed
[67]
tumor regression in patients with acute bacterial infections . After this observation, he decided to administer
[68]
inactivated Streptococcus pyogenes and Serratia marcescens - in a mixture he called Coley’s toxin - to a patient
with an inoperable sarcoma, inducing tumor regression and curing the patient [69-71] . Furthermore, it was used
[72]
in cases with carcinomas, lymphomas, melanomas and myelomas, having significant results .
The Coley’s toxin mechanism of action became a key finding for immunotherapy . It is composed of
[73]
gram-negative bacterial endotoxin (Serratia marcescens), a lipopolysaccharide released from the bacterial
cell membrane that was considered a prototype for pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs).
[74]
This compound induces the secretion of TNF, IL-2, INF-α and IL-12 from the immune system. Being
+
IL-12 the most important in both innate and adaptive immunities since it stimulates T-CD4 Th1 cells
[75]
+
development, and increases NK/NKT and TCD8 lymphocytes pathway mechanisms .
These pathways require Preexistent Immunization in order to gain antineoplastic activity. This comes from
[76]
expression of IL-12 receptors only on activated T cells , explaining its major effectiveness in patients with
[76]
previously sensitized T cells . On the other hand, bacterial intrinsic properties could also be used against
tumors, such as Streptokinase from Streptococcus pyogenes cases, an enzyme considered as one of the active
agents in Coley’s toxin. This enzyme has anti-angiogenic effects, suppressing new vessel formation and
[77]
decreasing tumor growth and invasion . Despite the fact that some clinical trials have shown effectiveness
[78]
with this therapy, others have not shown any success, presenting multiple reasons for treatment failures .
High doses of IL-12 used as support treatment with other cytokines have produced an immunologic
[74]
response with high toxicity and its employment has been cancelled .