Page 133 - Read Online
P. 133
Page 6 of 15 Sawayama et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2018;4:10 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2017.79
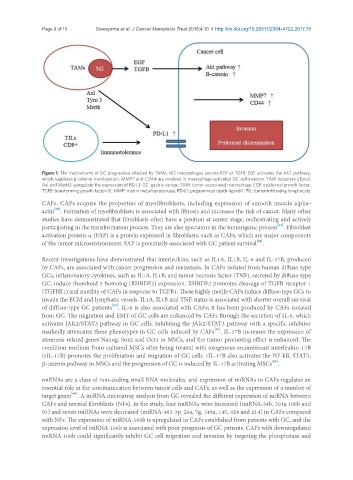
Figure 1. The mechanisms of GC progression affected by TAMs. M2 macrophages secrete EGF or TGFB. EGF activates the AKT pathway,
which regulates b-catenin translocation. MMP7 and CD44 are involved in macrophage-activated GC cell invasion. TAM receptors (Tyro3,
Axl and Mertk) upregulate the expression of PD-L1. GC: gastric cancer; TAM: tumor-associated macrophage; EGF: epidermal growth factor;
TGFB: transforming growth factor-b1; MMP: matrix metalloproteinase; PD-L1: programmed death-ligand-1; TIL: tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte
CAFs. CAFs acquire the properties of myofibroblasts, including expression of smooth muscle alpha-
[60]
actin . Formation of myofibroblasts is associated with fibrosis and increases the risk of cancer. Many other
studies have demonstrated that fibroblasts often have a position at center stage, orchestrating and actively
[61]
participating in the transformation process. They are also spectators in the tumorigenic process . Fibroblast
activation protein-a (FAP) is a protein expressed in fibroblasts, such as CAFs, which are major components
[62]
of the tumor microenvironment. FAP is potentially associated with GC patient survival .
Recent investigations have demonstrated that interleukins, such as IL1A, IL1B, IL-6 and IL-17B, produced
by CAFs, are associated with cancer progression and metastasis. In CAFs isolated from human diffuse-type
GCs, inflammatory cytokines, such as IL1A, IL1B, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF), secreted by diffuse-type
GC, induce rhomboid 5 homolog (RHBDF2) expression. RHBDF2 promotes cleavage of TGFB receptor 1
(TGFBR1) and motility of CAFs in response to TGFB1. These highly motile CAFs induce diffuse-type GCs to
invade the ECM and lymphatic vessels. IL1A, IL1B and TNF status is associated with shorter overall survival
[63]
of diffuse-type GC patients . IL-6 is also associated with CAFs; it has been produced by CAFs isolated
from GC. The migration and EMT of GC cells are enhanced by CAFs through the secretion of IL-6, which
activates JAK2/STAT3 pathway in GC cells. Inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 pathway with a specific inhibitor
[64]
markedly attenuates these phenotypes in GC cells induced by CAFs . IL-17B increases the expression of
stemness-related genes Nanog, Sox2 and Oct4 in MSCs, and the tumor promoting effect is enhanced. The
condition medium from cultured MSCs after being treated with exogenous recombinant interleukin-17B
(rIL-17B) promotes the proliferation and migration of GC cells. rIL-17B also activates the NF-kB, STAT3,
[65]
b-catenin pathway in MSCs and the progression of GC is induced by IL-17B activating MSCs .
miRNAs are a class of non-coding small RNA molecules, and expression of miRNAs in CAFs regulates an
essential role in the communication between tumor cells and CAFs, as well as the expression of a number of
[66]
target genes . A miRNA microarray analysis from GC revealed the different expression of miRNA between
CAFs and normal fibroblasts (NFs). In the study, four miRNAs were increased (miRNA-34b, 301a 106b and
93) and seven miRNAs were decreased (miRNA-483-3p, 26a, 7g, 148a, 145, 424 and 214) in CAFs compared
with NFs. The expression of miRNA-106b is upregulated in CAFs established from patients with GC, and the
expression level of miRNA-106b is associated with poor prognosis of GC patients. CAFs with downregulated
miRNA-106b could significantly inhibit GC cell migration and invasion by targeting the phosphatase and