Page 102 - Read Online
P. 102
Sugarbaker. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2018;4:7 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2017.67 Page 5 of 16
Z P
P I 2
Z P
Z P
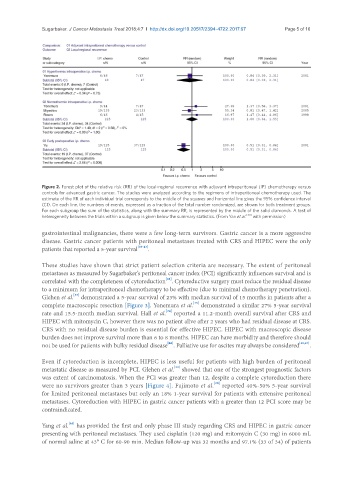
Figure 2. Forest plot of the relative risk (RR) of the local-regional recurrence with adjuvant intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy versus
controls for advanced gastric cancer. The studies were analyzed according to the regimens of intraperitoneal chemotherapy used. The
estimate of the RR of each individual trial corresponds to the middle of the squares and horizontal line gives the 95% confidence interval
(CI). On each line, the numbers of events, expressed as a fraction of the total number randomized, are shown for both treatment groups.
For each subgroup the sum of the statistics, along with the summary RR, is represented by the middle of the solid diamonds. A test of
heterogeneity between the trials within a subgroup is given below the summary statistics. (From Yan et al. [30] with permission)
gastrointestinal malignancies, there were a few long-term survivors. Gastric cancer is a more aggressive
disease. Gastric cancer patients with peritoneal metastases treated with CRS and HIPEC were the only
patients that reported a 5-year survival [39-43] .
These studies have shown that strict patient selection criteria are necessary. The extent of peritoneal
metastases as measured by Sugarbaker’s peritoneal cancer index (PCI) significantly influences survival and is
[44]
correlated with the completeness of cytoreduction . Cytoreductive surgery must reduce the residual disease
to a minimum for intraperitoneal chemotherapy to be effective (due to minimal chemotherapy penetration).
[33]
Glehen et al. demonstrated a 5-year survival of 23% with median survival of 15 months in patients after a
[45]
complete macroscopic resection [Figure 3]. Yonemura et al. demonstrated a similar 27% 5-year survival
[34]
rate and 15.5-month median survival. Hall et al. reported a 11.2-month overall survival after CRS and
HIPEC with mitomycin C, however there was no patient alive after 2 years who had residual disease at CRS.
CRS with no residual disease burden is essential for effective HIPEC. HIPEC with macroscopic disease
burden does not improve survival more than 6 to 8 months. HIPEC can have morbidity and therefore should
[46]
not be used for patients with bulky residual disease . Palliative use for ascites may always be considered [45,47] .
Even if cytoreduction is incomplete, HIPEC is less useful for patients with high burden of peritoneal
[33]
metastatic disease as measured by PCI. Glehen et al. showed that one of the strongest prognostic factors
was extent of carcinomatosis. When the PCI was greater than 12, despite a complete cytoreduction there
[20]
were no survivors greater than 3 years [Figure 4]. Fujimoto et al. reported 40%-50% 5-year survival
for limited peritoneal metastases but only an 18% 1-year survival for patients with extensive peritoneal
metastases. Cytoreduction with HIPEC in gastric cancer patients with a greater than 12 PCI score may be
contraindicated.
[46]
Yang et al. has provided the first and only phase III study regarding CRS and HIPEC in gastric cancer
presenting with peritoneal metastases. They used cisplatin (120 mg) and mitomycin C (30 mg) in 6000 mL
of normal saline at 43° C for 60-90 min. Median follow-up was 32 months and 97.1% (33 of 34) of patients