Page 91 - Read Online
P. 91
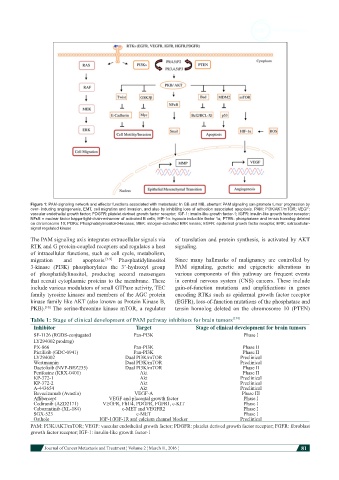
Figure 1: PAM-signaling network and effector functions associated with metastasis: In GB and MB, aberrant PAM signaling can promote tumor progression by
over- inducing angiogenesis, EMT, cell migration and invasion, and also by inhibiting loss of adhesion associated apoptosis. PAM: PI3K/AKT/mTOR; VEGF:
vascular endothelial growth factor; PDGFR: platelet derived growth factor receptor; IGF-1: insulin-like growth factor-1; IGFR: insulin-like growth factor receptor;
NFκB = nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; HIF-1α: hypoxia inducible factor 1α; PTEN: phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted
on chromosome 10; PI3Ks: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinases; MEK: mitogen-activated ERK kinase; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; ERK: extracellular-
signal regulated kinase
The PAM signaling axis integrates extracellular signals via of translation and protein synthesis, is activated by AKT
RTK and G protein-coupled receptors and regulates a host signaling.
of intracellular functions, such as cell cycle, metabolism,
migration and apoptosis. [7-9] Phosphatidylinositol Since many hallmarks of malignancy are controlled by
3-kinase (PI3K) phosphorylates the 3’-hydroxyl group PAM signaling, genetic and epigenetic alterations in
of phosphatidylinositol, producing second messengers various components of this pathway are frequent events
that recruit cytoplasmic proteins to the membrane. These in central nervous system (CNS) cancers. These include
include various modulators of small GTPase activity, TEC gain-of-function mutations and amplifications in genes
family tyrosine kinases and members of the AGC protein encoding RTKs such as epidermal growth factor receptor
kinase family like AKT (also known as Protein Kinase B, (EGFR), loss-of-function mutations of the phosphatase and
PKB). The serine-threonine kinase mTOR, a regulator tensin homolog deleted on the chromosome 10 (PTEN)
[10]
Table 1: Stage of clinical development of PAM pathway inhibitors for brain tumors [138]
Inhibitor Target Stage of clinical development for brain tumors
SF-1126 (RGDS-conjugated Pan-PI3K Phase I
LY294002 prodrug)
PX-866 Pan-PI3K Phase II
Pictilisib (GDC-0941) Pan-PI3K Phase II
LY294002 Dual PI3K/mTOR Preclinical
Wortmannin Dual PI3K/mTOR Preclinical
Dactolisib (NVP-BEZ235) Dual PI3K/mTOR Phase II
Perifosine (KRX-0401) Akt Phase II
KP-372-1 Akt Preclinical
KP-372-2 Akt Preclinical
A-443654 Akt Preclinical
Bevacizumab (Avastin) VEGF-A Phase III
Aflibercept VEGF and placental growth factor Phase I
Cediranib (AZD2171) VEGFR, Flt1/4, PDGFR, FGFR1, c-KIT Phase I
Cabozantinib (XL-184) c-MET and VEGFR2 Phase I
SGX-523 c-MET Phase I
Osthole IGF-1/IGF-1R and calcium channel blocker Preclinical
PAM: PI3K/AKT/mTOR; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor; PDGFR: platelet derived growth factor receptor; FGFR: fibroblast
growth factor receptor; IGF-1: insulin-like growth factor-1
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 2 ¦ March 11, 2016 ¦ 81