Page 378 - Read Online
P. 378
Mura et al. The peritoneal metastases from GC
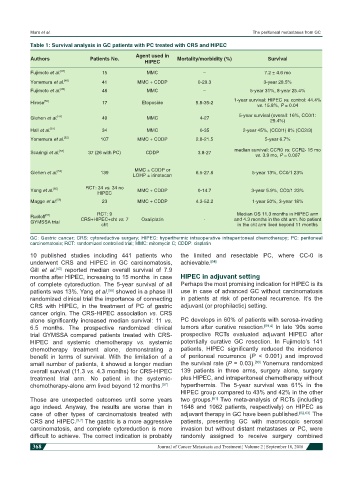
Table 1: Survival analysis in GC patients with PC treated with CRS and HIPEC
Agent used in
Authors Patients No. Mortality/morbidity (%) Survival
HIPEC
Fujimoto et al. [47] 15 MMC – 7.2 ± 4.6 mo
Yonemura et al. [48] 41 MMC + CDDP 0-29.3 3-year 28.5%
Fujimoto et al. [49] 48 MMC – 5-year 31%, 8-year 25.4%
Hirose [50] 17 Etoposide 5.8-35-2 1-year survival: HIPEC vs. control: 44.4%
vs. 15.8%, P = 0.04
Glehen et al. [44] 49 MMC 4-27 5-year survival (overall: 16%, CC0/1:
29.4%)
Hall et al. [51] 34 MMC 0-35 2-year 45%, (CC0/1) 8% (CC2/3)
Yonemura et al. [52] 107 MMC + CDDP 2.8-21.5 5-year 6.7%
Scaringi et al. [53] 37 (26 with PC) CDDP 3.8-27 median survival: CCR0 vs. CCR2- 15 mo
vs. 3.9 mo, P = 0.007
Glehen et al. [54] 139 MMC ± CDDP or 6.5-27.8 5-year 13%, CC0/1 23%
LOHP ± irinotecan
Yang et al. [55] RCT: 34 vs. 34 no MMC + CDDP 0-14.7 3-year 5.9%, CC0/1 23%
HIPEC
Magge et al. [56] 23 MMC + CDDP 4.3-52.2 1-year 50%, 3-year 18%
Median OS 11.3 months in HIPEC arm
RCT: 9
Rudloff [57] CRS+HIPEC+cht vs. 7 Oxaliplatin - and 4.3 months in the cht arm. No patient
GYMSSA trial
cht in the cht arm lived beyond 11 months
GC: Gastric cancer; CRS: cytoreductive surgery; HIPEC: hyperthermic intraoperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy; PC: peritoneal
carcinomatosis; RCT: randomized controlled trial; MMC: mitomycin C; CDDP: cisplatin
10 published studies including 441 patients who the limited and resectable PC, where CC-0 is
underwent CRS and HIPEC in GC carcinomatosis, achievable. [54]
Gill et al. reported median overall survival of 7.9
[43]
months after HIPEC, increasing to 15 months in case HIPEC in adjuvant setting
of complete cytoreduction. The 5-year survival of all Perhaps the most promising indication for HIPEC is its
patients was 13%. Yang et al. showed in a phase III use in case of advanced GC without carcinomatosis
[55]
randomized clinical trial the importance of connecting in patients at risk of peritoneal recurrence. It’s the
CRS with HIPEC, in the treatment of PC of gastric adjuvant (or prophilactic) setting.
cancer origin. The CRS-HIPEC association vs. CRS
alone significantly increased median survival: 11 vs. PC develops in 60% of patients with serosa-invading
6.5 months. The prospective randomized clinical tumors after curative resection. [59,4] In late ‘90s some
trial GYMSSA compared patients treated with CRS- prospective RCTs evaluated adjuvant HIPEC after
HIPEC and systemic chemotherapy vs. systemic potentially curative GC resection. In Fujimoto’s 141
chemotherapy treatment alone, demonstrating a patients, HIPEC significantly reduced the incidence
benefit in terms of survival. With the limitation of a of peritoneal recurrence (P < 0.001) and improved
[60]
small number of patients, it showed a longer median the survival rate (P = 0.03). Yonemura randomized
overall survival (11.3 vs. 4.3 months) for CRS-HIPEC 139 patients in three arms, surgery alone, surgery
treatment trial arm. No patient in the systemic- plus HIPEC, and intraperitoneal chemotherapy without
chemotherapy-alone arm lived beyond 12 months. [57] hyperthermia. The 5-year survival was 61% in the
HIPEC group compared to 43% and 42% in the other
Those are unexpected outcomes until some years two groups. Two meta-analysis of RCTs (including
[61]
ago indeed. Anyway, the results are worse than in 1648 and 1062 patients, respectively) on HIPEC as
case of other types of carcinomatosis treated with adjuvant therapy in GC have been published. [62,63] The
CRS and HIPEC. [5,7] The gastric is a more aggressive patients, presenting GC with macroscopic serosal
carcinomatosis, and complete cytoreduction is more invasion but without distant metastases or PC, were
difficult to achieve. The correct indication is probably randomly assigned to receive surgery combined
368 Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 2 ¦ September 18, 2016