Page 98 - Read Online
P. 98
Berghen et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2021;7:58 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2021.123 Page 5 of 10
Table 1. Overview of published trials on particle therapy in RCC
Study Type of Dose Med FU
Name (Ref.) Setting n DSS OS Toxicity
design treatment (BED) (mo)
[46]
Fukumitsu et al. Primary RCC, R Proton 22 Range 94- 37 100% 95% (3- Acute ≥ G2 in 5% (dermatitis),
unilateral 110 Gy (3-year) year) late ≥ G2 in 9% (renal
dysfunction)
[4]
Frick et al. Primary RCC, R Proton 1 48 Gy 12 100% 100% Acute G1 (GU, fatigue)
bilateral (1-year) (1-year)
[49]
Nomiya et al. Primary RCC, R CIRT 10 Range 86- 58 NR 74% (5- Late G4 in 10% (dermatitis)
unilateral 120 Gy year)
[50]
Kasuya et al. Primary RCC R CIRT 19 90 Gy 79 100% 89% (5- G4 in 21% (CKD) and G4 in
(5-year) year) 5% (dermatitis)
[51]
Kasuya et al. Primary RCC, P CIRT 8 Range 93- 43 100% NR Acute G1 (skin)
unilateral 104 Gy
[47]
Baydoun et al. Primary RCC, DA Photon vs. 10 Range 38- NA NA NA NA
unilateral proton 106 Gy
[48]
Thompson et al. Primary RCC, DA Photon vs. 3 151 Gy NA NA NA NA
unilateral proton
N: number; BED: biologically effective dose (for alpha/beta =10 Gy); RCC: renal cell carcinoma; med FU (mo): median follow-up (months); DSS:
disease-specific survival; OS: overall survival; R: retrospective study design; P: prospective study design; DA: dosimetric analysis; G: grade; Gy:
Gray (unit); GU: genito-urinary; NR: not reported; NA: not applicable; CIRT: carbon ion radiotherapy; CKD: chronic kidney disease.
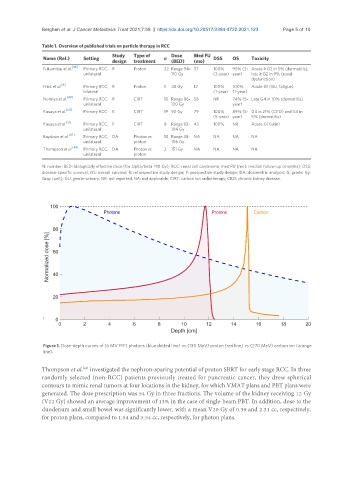
Figure 1. Dose-depth curves of (6 MV FFF) photons (blue dotted line) vs. (130 MeV) proton (red line) vs. (270 MeV) carbon ion (orange
line).
Thompson et al. investigated the nephron-sparing potential of proton SBRT for early stage RCC. In three
[48]
randomly selected (non-RCC) patients previously treated for pancreatic cancer, they drew spherical
contours to mimic renal tumors at four locations in the kidney, for which VMAT plans and PBT plans were
generated. The dose prescription was 54 Gy in three fractions. The volume of the kidney receiving 12 Gy
(V12 Gy) showed an average improvement of 13% in the case of single-beam PBT. In addition, dose to the
duodenum and small bowel was significantly lower, with a mean V20 Gy of 0.39 and 2.31 cc, respectively,
for proton plans, compared to 1.54 and 5.54 cc, respectively, for photon plans.