Page 49 - Read Online
P. 49
Dave et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:46 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.106 Page 11 of 36
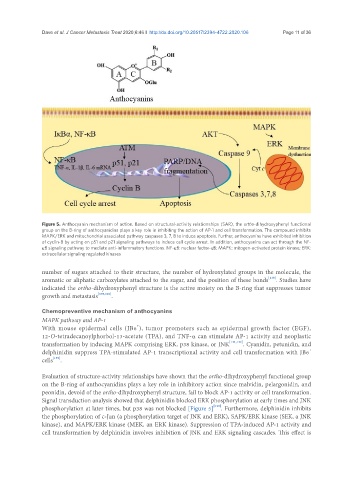
Figure 5. Anthocyanin mechanism of action. Based on structural-activity relationships (SAR), the ortho-dihydroxyphenyl functional
group on the B-ring of anthocyanidins plays a key role in inhibiting the action of AP-1 and cell transformation. The compound inhibits
MAPK/ERK and mitochondrial associated pathway caspases 3, 7, 8 to induce apoptosis. Further, anthocyanins have exhibited inhibition
of cyclin-B by acting on p51 and p21 signaling pathways to induce cell cycle arrest. In addition, anthocyanins can act through the NF-
κB signaling pathway to mediate anti-inflammatory functions. NF-κB: nuclear factor-κB; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK:
extracellular signaling regulated kinases
number of sugars attached to their structure, the number of hydroxylated groups in the molecule, the
aromatic or aliphatic carboxylates attached to the sugar, and the position of these bonds [138] . Studies have
indicated the ortho-dihydroxyphenyl structure is the active moiety on the B-ring that suppresses tumor
growth and metastasis [139,140] .
Chemopreventive mechanism of anthocyanins
MAPK pathway and AP-1
+
With mouse epidermal cells (JB6 ), tumor promoters such as epidermal growth factor (EGF),
12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), and TNF-α can stimulate AP-1 activity and neoplastic
transformation by inducing MAPK comprising ERK, p38 kinase, or JNK [141,142] . Cyanidin, petunidin, and
+
delphinidin suppress TPA-stimulated AP-1 transcriptional activity and cell transformation with JB6
cells [139] .
Evaluation of structure-activity relationships have shown that the ortho-dihydroxyphenyl functional group
on the B-ring of anthocyanidins plays a key role in inhibitory action since malvidin, pelargonidin, and
peonidin, devoid of the ortho-dihydroxyphenyl structure, fail to block AP-1 activity or cell transformation.
Signal transduction analysis showed that delphinidin blocked ERK phosphorylation at early times and JNK
phosphorylation at later times, but p38 was not blocked [Figure 5] [139] . Furthermore, delphinidin inhibits
the phosphorylation of c-Jun (a phosphorylation target of JNK and ERK), SAPK/ERK kinase (SEK, a JNK
kinase), and MAPK/ERK kinase (MEK, an ERK kinase). Suppression of TPA-induced AP-1 activity and
cell transformation by delphinidin involves inhibition of JNK and ERK signaling cascades. This effect is