Page 43 - Read Online
P. 43
Dave et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:46 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.106 Page 5 of 36
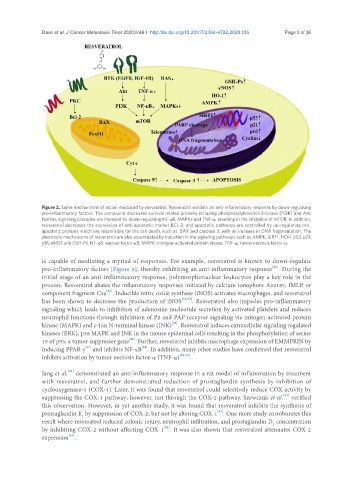
Figure 2. Some mechanisms of action mediated by resveratrol. Resveratrol exhibits an anti-inflammatory response by down-regulating
pro-inflammatory factors. The compound decreases survival related proteins including phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) and Akt.
Further, signaling cascades are impeded by down-regulating NF-κB, MAPKs and TNF-α, resulting in the inhibition of mTOR. In addition,
resveratrol decreases the expression of anti-apoptotic marker BCL-2, and apoptotic pathways are controlled by up-regulating pro-
apoptotic proteins which are responsible for the cell death, such as, BAX and caspase 3, with an increase in DNA fragmentation. The
pleotropic mechanisms of resveratrol are also accentuated by induction in the signaling pathways such as AMPK, SIRT1, HO-1, p53, p21,
p16, eNOS and GSH-Px. NF-κB: nuclear factor-κB; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α
is capable of mediating a myriad of responses. For example, resveratrol is known to down-regulate
[41]
pro-inflammatory factors [Figure 2], thereby exhibiting an anti-inflammatory response . During the
initial stage of an anti-inflammatory response, polymorphonuclear leukocytes play a key role in the
process. Resveratrol abates the inflammatory responses initiated by calcium ionophore A23187, fMLP, or
[42]
component fragment C5a . Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) activates macrophages, and resveratrol
has been shown to decrease the production of iNOS [43,44] . Resveratrol also impedes pro-inflammatory
signaling which leads to inhibition of adenosine nucleotide secretion by activated platelets and reduces
neutrophil functions through inhibition of P2 and PAP receptor signaling via mitogen-activated protein
[45]
kinase (MAPK) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) . Resveratrol induces extracellular signaling regulated
kinases (ERK), p38 MAPK and JNK in the mouse epidermal cells resulting in the phosphorylation of serine
[46]
15 of p53, a tumor suppresser gene . Further, resveratrol inhibits macrophage expression of EMMPRIN by
[47]
inducing PPAR-γ and inhibits NF-κB . In addition, many other studies have confirmed that resveratrol
[48]
inhibits activation by tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) [49-51] .
[36]
Jang et al. demonstrated an anti-inflammatory response in a rat model of inflammation by treatment
with resveratrol, and further demonstrated reduction of prostaglandin synthesis by inhibition of
cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1). Later, it was found that resveratrol could selectively reduce COX activity by
suppressing the COX-1 pathway; however, not through the COX-2 pathway. Szewczuk et al. verified
[52]
this observation. However, in yet another study, it was found that resveratrol inhibits the synthesis of
[53]
prostaglandin E by suppression of COX-2, but not by altering COX-1 . One more study corroborates this
2
result where resveratrol reduced colonic injury, neutrophil infiltration, and prostaglandin D concentration
2
by inhibiting COX-2 without affecting COX-1 . It was also shown that resveratrol attenuates COX-2
[54]
[53]
expression .