Page 9 - Read Online
P. 9
Santoni et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:22 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.49 Page 5 of 14
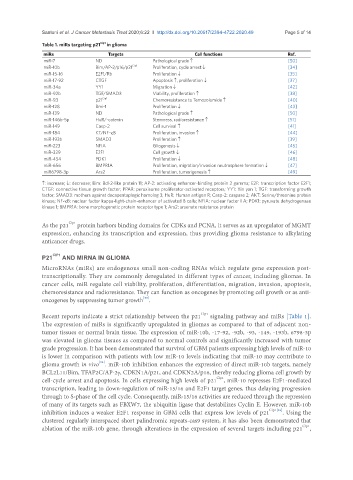
Table 1. miRs targeting p21 Cip1 in glioma
miRs Targets Cell functions Ref.
miR-7 ND Pathological grade ↑ [50]
miR-10b Bim/AP-2/p16/p21 Cip1 Proliferation, cycle arrest ↓ [34]
miR-15-16 E2F1/Rb Proliferation ↓ [35]
miR-17-92 CTGF Apoptosis ↑, proliferation ↓ [37]
miR-34a YY1 Migration ↓ [42]
miR-92b TGF/SMAD3 Viability, proliferation ↑ [38]
miR-93 p21 Cip1 Chemoresistance to Temozolomide ↑ [40]
miR-128 Bmi-1 Proliferation ↓ [43]
miR-139 ND Pathological grade ↑ [50]
miR-146b-5p HuR/-catenin Stemness, radioresistance ↑ [51]
miR-149 Casp-2 Cell survival ↑ [41]
miR-184 KT/NF-κB Proliferation, invasion ↑ [44]
miR-193b SMAD3 Proliferation ↑ [39]
miR-223 NFIA Gliogenesis ↓ [45]
miR-329 E2F1 Cell growth ↓ [46]
miR-454 PDK1 Proliferation ↓ [48]
miR-656 BMPR1A Proliferation, migration/invasion neutrosphere formation ↓ [47]
miR6798-3p Ars2 Proliferation, tumorigenesis ↑ [49]
↑: increase; ↓: decrease; Bim: Bcl-2-like protein 11; AP-2: activating enhancer-binding protein 2 gamma; E2F: transcription factor E2F1;
CTGF: connective tissue growth factor; PPAR: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors; YY1: Yin yan 1; TGF: transforming growth
factor; SMAD3: mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3; HuR: Human antigen R; Casp-2: caspase 2; AKT: Serine/threonine protein
kinase; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NFIA: nuclear factor I A; PDK1: pyruvate dehydrogenase
kinase 1; BMPR1A: bone morphogenetic protein receptor type 1; Ars2: arsenate resistance protein
Cip1
As the p21 protein harbors binding domains for CDKs and PCNA, it serves as an upregulator of MGMT
expression, enhancing its transcription and expression, thus providing glioma resistance to alkylating
anticancer drugs.
CIP1
P21 AND MIRNA IN GLIOMA
MicroRNAs (miRs) are endogenous small non-coding RNAs which regulate gene expression post-
transcriptionally. They are commonly deregulated in different types of cancer, including gliomas. In
cancer cells, miR regulate cell viability, proliferation, differentiation, migration, invasion, apoptosis,
chemoresistance and radioresistance. They can function as oncogenes by promoting cell growth or as anti-
[33]
oncogenes by suppressing tumor growth .
Cip1
Recent reports indicate a strict relationship between the p21 signaling pathway and miRs [Table 1].
The expression of miRs is significantly upregulated in gliomas as compared to that of adjacent non-
tumor tissues or normal brain tissue. The expression of miR-10b, -17-92, -92b, -93, -149, -193b, 6798-3p
was elevated in glioma tissues as compared to normal controls and significantly increased with tumor
grade progression. It has been demonstrated that survival of GBM patients expressing high levels of miR-10
is lower in comparison with patients with low miR-10 levels indicating that miR-10 may contribute to
[34]
glioma growth in vivo . miR-10b inhibition enhances the expression of direct miR-10b targets, namely
BCL2L11/Bim, TFAP2C/AP-2γ, CDKN1A/p21, and CDKN2A/p16, thereby reducing glioma cell growth by
cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis. In cells expressing high levels of p21 , miR-10 represses E2F1-mediated
Cip1
transcription, leading to down-regulation of miR-15/16 and E2F1 target genes, thus delaying progression
through to S-phase of the cell cycle. Consequently, miR-15/16 activities are reduced through the repression
of many of its targets such as FBXW7, the ubiquitin ligase that destabilizes Cyclin E. However, miR-10b
inhibition induces a weaker E2F1 response in GBM cells that express low levels of p21 Cip1[35] . Using the
clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats-cas9 system, it has also been demonstrated that
Cip1
ablation of the miR-10b gene, through alterations in the expression of several targets including p21 ,