Page 9 - Read Online
P. 9
Gauduchon et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:72 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.023 Page 3 of 9
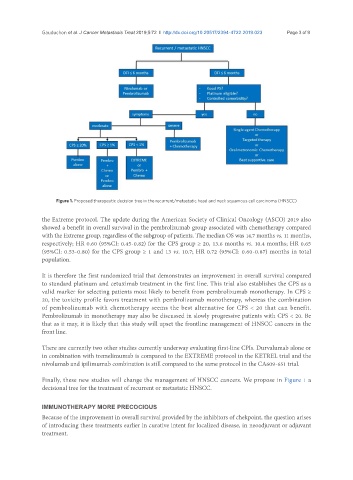
Figure 1. Proposed therapeutic decision tree in the recurrent/metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC)
the Extreme protocol. The update during the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) 2019 also
showed a benefit in overall survival in the pembrolizumab group associated with chemotherapy compared
with the Extreme group, regardless of the subgroup of patients. The median OS was 14.7 months vs. 11 months,
respectively; HR 0.60 (95%CI: 0.45-0.82) for the CPS group ≥ 20, 13.6 months vs. 10.4 months; HR 0.65
(95%CI: 0.53-0.80) for the CPS group ≥ 1 and 13 vs. 10.7; HR 0.72 (95%CI: 0.60-0.87) months in total
population.
It is therefore the first randomized trial that demonstrates an improvement in overall survival compared
to standard platinum and cetuximab treatment in the first line. This trial also establishes the CPS as a
valid marker for selecting patients most likely to benefit from pembrolizumab monotherapy. In CPS ≥
20, the toxicity profile favors treatment with pembrolizumab monotherapy, whereas the combination
of pembrolizumab with chemotherapy seems the best alternative for CPS < 20 that can benefit.
Pembrolizumab in monotherapy may also be discussed in slowly progressive patients with CPS < 20. Be
that as it may, it is likely that this study will upset the frontline management of HNSCC cancers in the
front line.
There are currently two other studies currently underway evaluating first-line CPIs. Durvalumab alone or
in combination with tremelimumab is compared to the EXTREME protocol in the KETREL trial and the
nivolumab and ipilimumab combination is still compared to the same protocol in the CA609-651 trial.
Finally, these new studies will change the management of HNSCC cancers. We propose in Figure 1 a
decisional tree for the treatment of recurrent or metastatic HNSCC.
IMMUNOTHERAPY MORE PRECOCIOUS
Because of the improvement in overall survival provided by the inhibitors of chekpoint, the question arises
of introducing these treatments earlier in curative intent for localized disease, in neoadjuvant or adjuvant
treatment.