Page 286 - Read Online
P. 286
Page 2 of 16 Lei et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:38 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.12
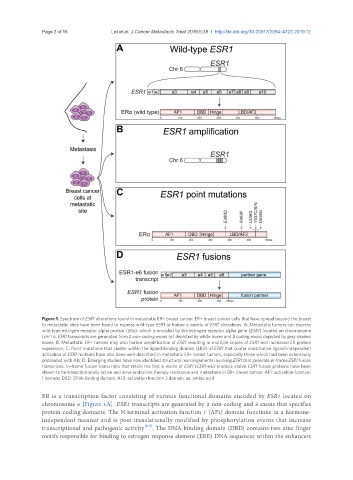
Figure 1. Spectrum of ESR1 alterations found in metastatic ER+ breast cancer. ER+ breast cancer cells that have spread beyond the breast
to metastatic sties have been found to express wild-type ESR1 or harbor a variety of ESR1 alterations. A: Metastatic tumors can express
wild-type estrogen receptor alpha protein (ERa), which is encoded by the estrogen receptor alpha gene (ESR1) located on chromosome
(chr) 6. ESR1 transcripts are generated from 2 non-coding exons (e) depicted by white boxes and 8 coding exons depicted by gray shaded
boxes; B: Metastatic ER+ tumors may also harbor amplification of ESR1 resulting in multiple copies of ESR1 and increased ER protein
expression; C: Point mutations that cluster within the ligand-binding domain (LBD) of ESR1 that confer constitutive ligand-independent
activation of ESR1 mutants have also been well-described in metastatic ER+ breast tumors, especially those which had been extensively
pretreated with AIs; D: Emerging studies have now identified structural rearrangements involving ESR1 that generate in-frame ESR1 fusion
transcripts. In-frame fusion transcripts that retain the first 6 exons of ESR1 (ESR1-e6) produce stable ESR1 fusion proteins have been
shown to be transcriptionally active and drive endocrine therapy resistance and metastasis in ER+ breast cancer. AF1: activation function
1 domain; DBD: DNA-binding domain; AF2: activation function 2 domain; aa: amino acid
ER is a transcription factor consisting of various functional domains encoded by ESR1 located on
chromosome 6 [Figure 1A]. ESR1 transcripts are generated by 2 non-coding and 8 exons that specifies
protein-coding domains. The N-terminal activation function 1 (AF1) domain functions in a hormone-
independent manner and is post-translationally modified by phosphorylation events that increase
transcriptional and pathogenic activity [2-5] . The DNA-binding domain (DBD) contains two zinc finger
motifs responsible for binding to estrogen response element (ERE) DNA sequences within the enhancers