Page 19 - Read Online
P. 19
Page 6 of 12 Kirakli et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:10 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.73
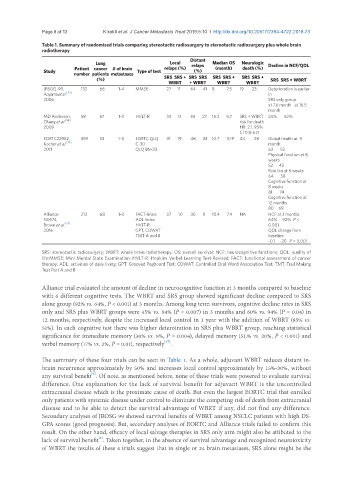
Table 1. Summary of randomised trials comparing stereotactic radiosurgery to stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole brain
radiotherapy
Distant
Lung Local relaps Median OS Neurologic Decline in NCF/QOL
Patient cancer # of brain relaps (%) (month) death (%)
Study Type of test (%)
number patients metastases
(%) SRS SRS + SRS SRS SRS SRS + SRS SRS + SRS SRS + WBRT
WBRT + WBRT WBRT WBRT
JRSOG-99, 132 66 1-4 MMSE 27 11 64 41 8 7.5 19 23 Deterioration is earlier
Aoyama et al. [33] in
2006 SRS only gorup
at 7.6 month at 16.5
month
MD Anderson, 58 67 1-3 HVLT-R 33 0 55 27 15.2 5.7 SRS + WBRT 24% 52%
Chang et al. [34] risk for death
2009 HR: 2.1, 95%
CI 0.8-6.0
EORTC22952, 359 53 1-3 EORTC QLQ 31 19 48 33 10.7 10.9 44 28 Global health at 9
Kocher et al. [35] C-30 month.
2011 QLQ BN-20 63 52
Physical function at 8
weeks
52 42
Role fxn at 8 weeks
64 58
Cognitive function at
8 weeks
81 74
Cognitive function at
12 months
80 69
Alliance 213 68 1-3 FACT-Brain 27 10 30 8 10.4 7.4 NA NCF at 3 months
N0574, ADL Index 64% 92% P <
Brown et al. [37] HVLT-R 0.001
2016 GPT, COWAT QOL change from
TMT-A and B baseline
-0.1 -20 P = 0.001
SRS: stereotactic radiosurgery; WBRT: whole brain radiotherapy; OS: overall survival; NCF: neurocognitive functions; QOL: quality of
life;MMSE: Mini Mental State Examination; HVLT-R: Hopkins Verbal Learning Test-Revised; FACT: functional assessment of cancer
therapy; ADL: activities of daily living; GPT: Grooved Pegboard Test; COWAT: Controlled Oral Word Association Test; TMT: Trail Making
Test Part A and B
Alliance trial evaluated the amount of decline in neurocognitive function at 3 months compared to baseline
with 6 different cognitive tests. The WBRT and SRS group showed significant decline compared to SRS
alone group (92% vs. 64%, P < 0.001) at 3 months. Among long term survivors, cognitive decline rates in SRS
only and SRS plus WBRT groups were 45% vs. 94% (P = 0.007) in 3 months and 60% vs. 94% (P = 0.04) in
12 months, respectively, despite the increased local control in 1 year with the addition of WBRT (85% vs.
51%). In each cognitive test there was higher deteroiration in SRS plus WBRT group, reaching statistical
significance for immediate memory (30% vs. 8%, P = 0.004), delayed memory (51.% vs. 20%, P < 0.001) and
[37]
verbal memory (17% vs. 2%, P = 0.01), respectively .
The summary of these four trials can be seen in Table 1. As a whole, adjuvant WBRT reduces distant in-
brain recurrence approximately by 50% and increases local control approximately by 15%-30%, without
[6]
any survival benefit . Of note, as mentioned before, none of these trials were powered to evaluate survival
difference. One explanation for the lack of survival benefit for adjuvant WBRT is the uncontrolled
extracranial disease which is the proximate cause of death. But even the largest EORTC trial that enrolled
only patients with systemic disease under control to eliminate the competing risk of death from extracranial
disease and to be able to detect the survival advantage of WBRT if any, did not find any difference.
Secondary analyses of JROSG 99 showed survival benefits of WBRT among NSCLC patients with high DS-
GPA scores (good prognosis). But, secondary analyses of EORTC and Alliance trials failed to confirm this
result. On the other hand, efficacy of local salvage therapies in SRS only arm might also be attibuted to the
[6]
lack of survival benefit . Taken together, in the absence of survival advantage and recognized neurotoxicity
of WBRT the results of these 4 trials suggest that in single or 24 brain metastases, SRS alone might be the