Page 27 - Read Online
P. 27
Zhou et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2018;4:41 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.16 Page 7 of 15
A
B
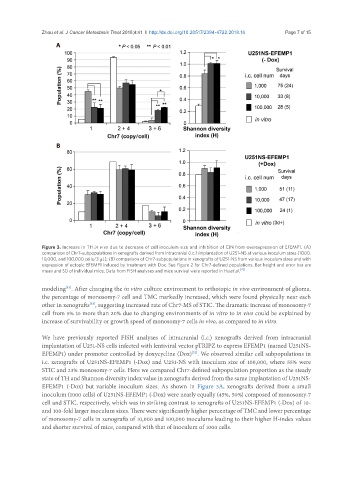
Figure 3. Increase in TH in vivo due to decrease of cell inoculum size and inhibition of CIN from overexpression of EFEMP1. (A)
comparison of Chr7-subpopulations in xenografts derived from intracranial (i.c.) implantation of U251-NS at various inoculum sizes (1000,
10,000, and 100,000 cells/3 mL); (B) comparison of Chr7-subpopulations in xenografts of U251-NS from various inoculum sizes and with
expression of ectopic EFEMP1 induced by treatment with Dox. See Figure 2 for Chr7-defined populations. Bar height and error bar are
mean and SD of individual mice. Data from FISH analyses and mice survival were reported in Hu et al. [32]
modeling . After changing the in vitro culture environment to orthotopic in vivo environment of glioma,
[13]
the percentage of monosomy-7 cell and TMC markedly increased, which were found physically near each
other in xenografts , suggesting increased rate of Chr7-MS of STIC. The dramatic increase of monosomy-7
[13]
cell from 5% to more than 20% due to changing environments of in vitro to in vivo could be explained by
increase of survivability or growth speed of monosomy-7 cells in vivo, as compared to in vitro.
We have previously reported FISH analyses of intracranial (i.c.) xenografts derived from intracranial
implantation of U251-NS cells infected with lentiviral vector pTRIPZ to express EFEMP1 (named U251NS-
EFEMP1) under promoter controlled by doxycycline (Dox) . We observed similar cell subpopulations in
[32]
i.c. xenografts of U251NS-EFEMP1 (-Dox) and U251-NS with inoculum size of 100,000, where 55% were
STIC and 23% monosomy-7 cells. Here we compared Chr7-defined subpopulation proportion as the steady
state of TH and Shannon diversity index value in xenografts derived from the same implantation of U251NS-
EFEMP1 (-Dox) but variable inoculum sizes. As shown in Figure 3A, xenografts derived from a small
inoculum (1000 cells) of U251NS-EFEMP1 (-Dox) were nearly equally (45%, 50%) composed of monosomy-7
cell and STIC, respectively, which was in striking contrast to xenografts of U251NS-EFEMP1 (-Dox) of 10-
and 100-fold larger inoculum sizes. There were significantly higher percentage of TMC and lower percentage
of monosomy-7 cells in xenografts of 10,000 and 100,000 inoculums leading to their higher H-index values
and shorter survival of mice, compared with that of inoculum of 1000 cells.