Page 131 - Read Online
P. 131
Nakamura et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2018;4:32 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2017.78 Page 3 of 11
Table 1. CTC enrichment and detection technologies
Method System Principle Limitations
Enrichment technologies
Biological CellSearch EpCAM antibodies coated with ferrofluid beads Dependent on EpCAM
AdnaTest Immunomagnetic detection of EpCAM High rate of false positive
CTC-chip EpCAM antibodies coated with microposts Dependent on EpCAM
MACS Immunomagnetic beads coated with EpCAM antibodies Dependent on EpCAM
MagSweeper Immunomagnetic beads coated with EpCAM antibodies Dependent on EpCAM
Physical ISET Size Variations in cell size
OncoQuik Density Loss of CTCs
RosetteSep Density, negative selection Loss of CTCs
Detection technologies
Immunocytological FACS Antigen expression optical Limited throughput
FAST Antigen expression optical Loss of CTCs
FISH Detects chromosomal DNA sequence Loss of vibility
Molecular RT-PCR Measures nucleic acid High rate of false positive
Functional assay EPISPOT Antigen expression Enzymatic activity varies
CTC: circulating tumor cell; EpCAM: epithelial cells adhesion molecule; MACS: magnetic activated cell sorting; ISET: isolation by size
of epithelial tumor; FACS: fluoroscence-assited cell sorting; FAST: fiber-optic array scanning technology; FISH: fluorescence in situ
hybridization; RT-PCR: reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; EPISPOT: epithelial immunospot
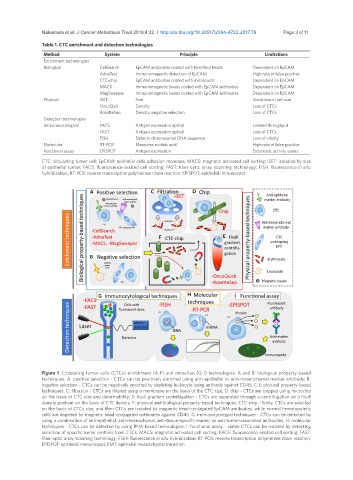
A C D
Anti-epithelial
Magnetic beads Anti-mesenchymal marker antibody
marker antibody
Anti-epithelial
marker antibody
CTC
Leukocyte Anti-mesenchymal
CTC
CTC undergoing EMT marker antibody
Erythrocyte
F E CTC
undergoing
EMT
B
Erythrocyte
Antibody
against
CD45
Leukocyte
Magnetic beads
CTC
G H I
Cells with Fluorescent
fluorescent dyes antibody
CTC Protein
CTC
CTC
Emission Anti-marker
antibody
Immunospots
Figure 1. Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) enrichment (A-F) and detection (G-I) technologies. A and B: biological property-based
techniques. A: positive selection - CTCs can be positively enriched using anti-epithelial or anti-mesenchymal marker antibody; B:
negative selection - CTCs can be negatively enriched by depleting leukocyte using antibody against CD45. C-E: physical property-based
techniques. C: filtration - CTCs are filtered using a membrane on the basis of the CTC size; D: chip - CTCs are trapped using microchip
on the basis of CTC size and deformability; E: ficoll gradient centrifugation - CTCs are separated through a centrifugation on a ficoll
density gradient on the basis of CTC density. F: physical and biological property-based techniques, CTC-chip - firstly, CTCs are selected
on the basis of CTCs size, and then CTCs are isolated by magnetic bead-conjugated EpCAM antibodies, while normal hematopoietic
cells are depleted by magnetic bead-conjugated antibodies against CD45. G: immunocytologial techniques - CTCs can be detected by
using a combination of anti-epithelial, anti-mesenchymal, anti-tissue-specific marker, or anti-tumor-associated antibodies. H: molecular
techniques - CTCs can be detected by using RNA-based technologies. I: functional assay - viable CTCs can be isolated by detecting
secretion of specific tumor proteins from CTCs. MACS: magnetic activated cell sorting; FACS: fluoroscence-assited cell sorting; FAST:
fiber-optic array scanning technology; FISH: fluorescence in situ hybridization; RT-PCR: reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction;
EPISPOT: epithelial immunospot; EMT: epithelial mesenchymal transition