Page 25 - Read Online
P. 25
Potdar CTCs in cancer diagnosis and treatment
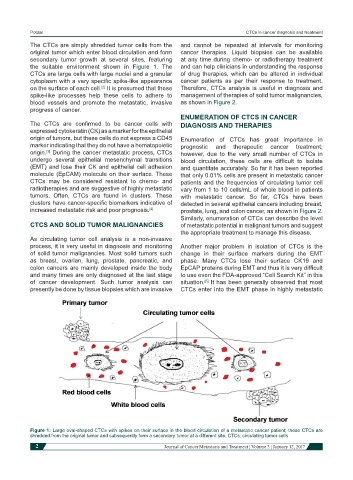
The CTCs are simply shredded tumor cells from the and cannot be repeated at intervals for monitoring
original tumor which enter blood circulation and form cancer therapies. Liquid biopsies can be available
secondary tumor growth at several sites, featuring at any time during chemo- or radiotherapy treatment
the suitable environment shown in Figure 1. The and can help clinicians in understanding the response
CTCs are large cells with large nuclei and a granular of drug therapies, which can be altered in individual
cytoplasm with a very specific spike-like appearance cancer patients as per their response to treatment.
on the surface of each cell. It is presumed that these Therefore, CTCs analysis is useful in diagnosis and
[2]
spike-like processes help these cells to adhere to management of therapies of solid tumor malignancies,
blood vessels and promote the metastatic, invasive as shown in Figure 2.
progress of cancer.
ENUMERATION OF CTCS IN CANCER
The CTCs are confirmed to be cancer cells with DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPIES
expressed cytokeratin (CK) as a marker for the epithelial
origin of tumors, but these cells do not express a CD45 Enumeration of CTCs has great importance in
marker indicating that they do not have a hematopoietic prognostic and therapeutic cancer treatment;
origin. During the cancer metastatic process, CTCs however, due to the very small number of CTCs in
[3]
undergo several epithelial mesenchymal transitions blood circulation, these cells are difficult to isolate
(EMT) and lose their CK and epithelial cell adhesion and quantitate accurately. So far it has been reported
molecule (EpCAM) molecule on their surface. These that only 0.01% cells are present in metastatic cancer
CTCs may be considered resistant to chemo- and patients and the frequencies of circulating tumor cell
radiotherapies and are suggestive of highly metastatic vary from 1 to 10 cells/mL of whole blood in patients
tumors. Often, CTCs are found in clusters. These with metastatic cancer. So far, CTCs have been
clusters have cancer-specific biomarkers indicative of detected in several epithelial cancers including breast,
increased metastatic risk and poor prognosis. [4] prostate, lung, and colon cancer, as shown in Figure 2.
Similarly, enumeration of CTCs can describe the level
CTCS AND SOLID TUMOR MALIGNANCIES of metastatic potential in malignant tumors and suggest
the appropriate treatment to manage this disease.
As circulating tumor cell analysis is a non-invasive
process, it is very useful in diagnosis and monitoring Another major problem in isolation of CTCs is the
of solid tumor malignancies. Most solid tumors such change in their surface markers during the EMT
as breast, ovarian, lung, prostate, pancreatic, and phase. Many CTCs lose their surface CK19 and
colon cancers are mainly developed inside the body EpCAP proteins during EMT and thus it is very difficult
and many times are only diagnosed at the last stage to use even the FDA-approved “Cell Search Kit” in this
of cancer development. Such tumor analysis can situation. It has been generally observed that most
[5]
presently be done by tissue biopsies which are invasive CTCs enter into the EMT phase in highly metastatic
Figure 1: Large oval-shaped CTCs with spikes on their surface in the blood circulation of a metastatic cancer patient; these CTCs are
shredded from the original tumor and subsequently form a secondary tumor at a different site. CTCs: circulating tumor cells
2 Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 3 ¦ January 12, 2017