Page 262 - Read Online
P. 262
Page 8 of 18 Qin et al. Hepatoma Res 2020;6:24 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2020.04
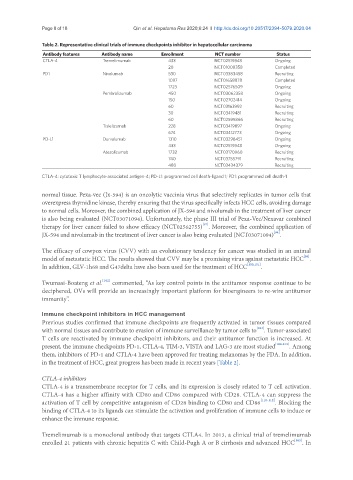
Table 2. Representative clinical trials of immune checkpoints inhibitor in hepatocellular carcinoma
Antibody features Antibody name Enrollment NCT number Status
CTLA-4 Tremelimumab 433 NCT02519348 Ongoing
20 NCT01008358 Completed
PD1 Nivolumab 530 NCT03383458 Recruiting
1097 NCT01658878 Completed
1723 NCT02576509 Ongoing
Pembrolizumab 450 NCT03062358 Ongoing
150 NCT02702414 Ongoing
60 NCT03163992 Recruiting
30 NCT03419481 Recruiting
60 NCT02595866 Recruiting
Tislelizumab 228 NCT03419897 Ongoing
674 NCT03412773 Ongoing
PD-L1 Durvalumab 1310 NCT03298451 Ongoing
433 NCT02519348 Ongoing
Atezolizumab 1732 NCT03170960 Recruiting
740 NCT03755791 Recruiting
480 NCT03434379 Recruiting
CTLA-4: cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4; PD-L1: programmed cell death-ligand 1; PD1: programmed cell death-1
normal tissue. Pexa-vec (Jx-594) is an oncolytic vaccinia virus that selectively replicates in tumor cells that
overexpress thymidine kinase, thereby ensuring that the virus specifically infects HCC cells, avoiding damage
to normal cells. Moreover, the combined application of JX-594 and nivolumab in the treatment of liver cancer
is also being evaluated (NCT03071094). Unfortunately, the phase III trial of Pexa-Vec/Nexavar combined
[97]
therapy for liver cancer failed to show efficacy (NCT02562755) . Moreover, the combined application of
JX-594 and nivolumab in the treatment of liver cancer is also being evaluated (NCT03071094) .
[98]
The efficacy of cowpox virus (CVV) with an evolutionary tendency for cancer was studied in an animal
[99]
model of metastatic HCC. The results showed that CVV may be a promising virus against metastatic HCC .
In addition, GLV-1h68 and G47delta have also been used for the treatment of HCC [100,101] .
Twumasi-Boateng et al. [102] commented, “As key control points in the antitumor response continue to be
deciphered, OVs will provide an increasingly important platform for bioengineers to re-wire antitumor
immunity”.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors in HCC management
Previous studies confirmed that immune checkpoints are frequently activated in tumor tissues compared
with normal tissues and contribute to evasion of immune surveillance by tumor cells to [103] . Tumor-associated
T cells are reactivated by immune checkpoint inhibitors, and their antitumor function is increased. At
present, the immune checkpoints PD-1, CTLA-4, TIM-3, VISTA and LAG-3 are most studied [104-109] . Among
them, inhibitors of PD-1 and CTLA-4 have been approved for treating melanomas by the FDA. In addition,
in the treatment of HCC, great progress has been made in recent years [Table 2].
CTLA-4 inhibitors
CTLA-4 is a transmembrane receptor for T cells, and its expression is closely related to T cell activation.
CTLA-4 has a higher affinity with CD80 and CD86 compared with CD28. CTLA-4 can suppress the
activation of T cell by competitive antagonism of CD28 binding to CD80 and CD86 [110-112] . Blocking the
binding of CTLA-4 to its ligands can stimulate the activation and proliferation of immune cells to induce or
enhance the immune response.
Tremelimumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets CTLA4. In 2013, a clinical trial of tremelimumab
enrolled 21 patients with chronic hepatitis C with Child-Pugh A or B cirrhosis and advanced HCC [105] . In