Page 305 - Read Online
P. 305
Page 4 of 6 Hu et al. Hepatoma Res 2019;5:29 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2019.23
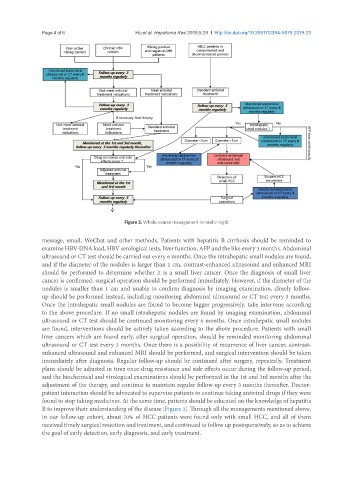
Figure 3. Whole-course management-no end in sight
message, email, WeChat and other methods. Patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis should be reminded to
examine HBV-DNA load, HBV serological tests, liver function, AFP and the like every 3 months. Abdominal
ultrasound or CT test should be carried out every 6 months. Once the intrahepatic small nodules are found,
and if the diameter of the nodules is larger than 1 cm, contrast-enhanced ultrasound and enhanced MRI
should be performed to determine whether it is a small liver cancer. Once the diagnosis of small liver
cancer is confirmed, surgical operation should be performed immediately. However, if the diameter of the
nodules is smaller than 1 cm and unable to confirm diagnosis by imaging examination, closely follow-
up should be performed instead, including monitoring abdominal ultrasound or CT test every 3 months.
Once the intrahepatic small nodules are found to become bigger progressively, take intervene according
to the above procedure. If no small intrahepatic nodules are found by imaging examination, abdominal
ultrasound or CT test should be continued monitoring every 6 months. Once intrahepatic small nodules
are found, interventions should be actively taken according to the above procedure. Patients with small
liver cancers which are found early, after surgical operation, should be reminded monitoring abdominal
ultrasound or CT test every 3 months. Once there is a possibility of recurrence of liver cancer, contrast-
enhanced ultrasound and enhanced MRI should be performed, and surgical intervention should be taken
immediately after diagnosis. Regular follow-up should be continued after surgery, repeatedly. Treatment
plans should be adjusted in time once drug resistance and side effects occur during the follow-up period,
and the biochemical and virological examinations should be performed in the 1st and 3rd months after the
adjustment of the therapy, and continue to maintain regular follow-up every 3 months thereafter. Doctor-
patient interaction should be advocated to supervise patients to continue taking antiviral drugs if they were
found to stop taking medicines. At the same time, patients should be educated on the knowledge of hepatitis
B to improve their understanding of the disease [Figure 3]. Through all the managements mentioned above,
in our follow-up cohort, about 70% of HCC patients were found only with small HCC, and all of them
received timely surgical resection and treatment, and continued to follow up postoperatively, so as to achieve
the goal of early detection, early diagnosis, and early treatment.